Why is address verification important under AML Customer Due Diligence
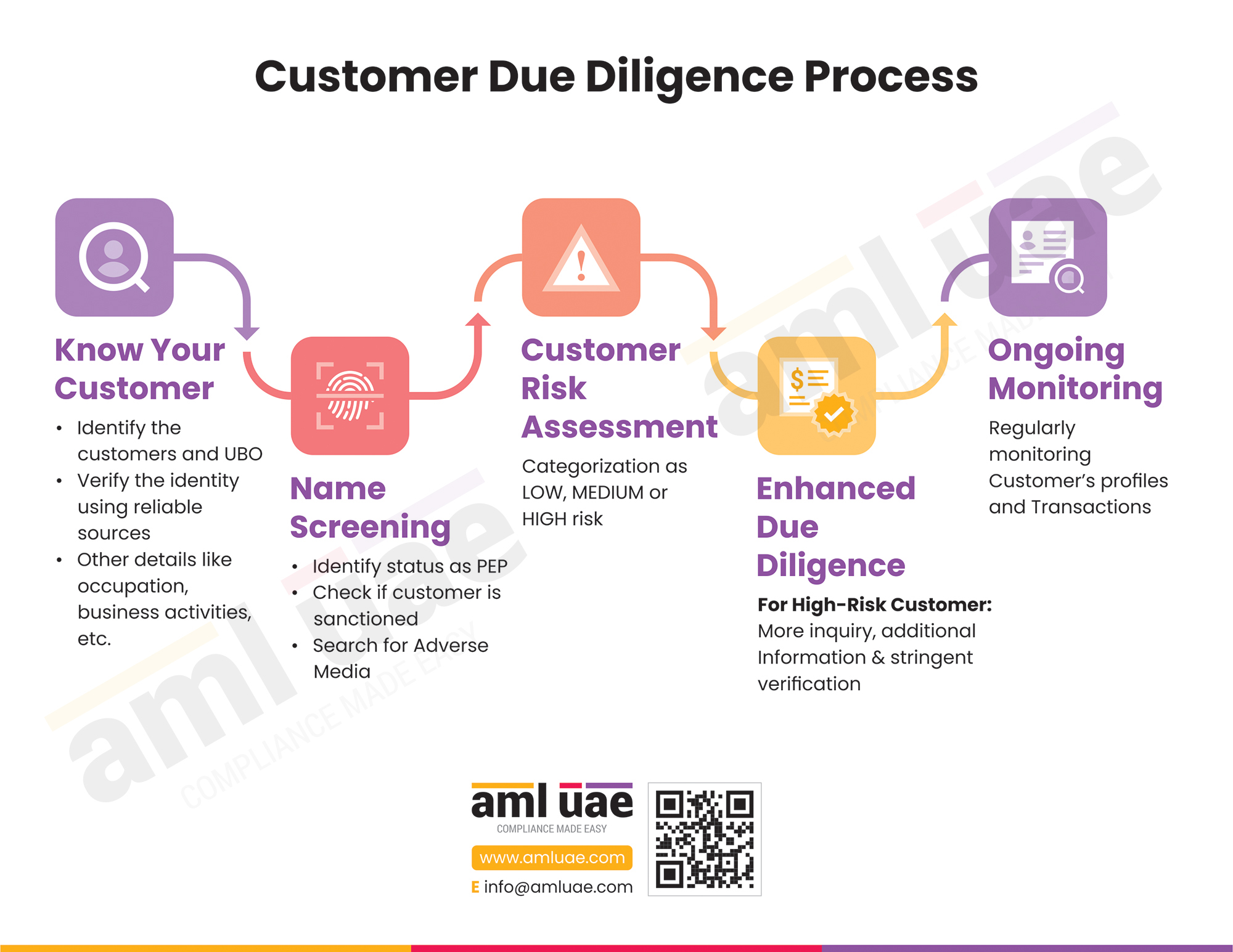
Customer Due Diligence is a critical aspect of the Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Program, aiming to identify the customer and the beneficial owners. One essential component of the Customer Due Diligence (CDD) process is obtaining the customer’s address details and verifying the same using reliable, independent sources.
Through this article, we shall explore why address verification is considered an important AML measure to detect red flags and discuss the right approach to adequately complete the address verification measures.
Understanding the importance of Address Verification
The UAE AML laws mandate regulated entities to design and deploy robust measures to combat financial crime. CDD is a crucial AML measure aimed at examining the genuineness of the customer and uncovering money laundering or terrorism financing instances attempts. During CDD, regulated entities must enquire about the customer’s place of domicile, business, etc. It is vital to examine the accuracy of the address details furnished by the customer. Here comes the implementation of the “address verification” process.
Address verification is a check performed to determine the realism of the customer’s address (business or residential). It is important to confirm that the customer can be traced to this address for any transactional correspondence or other requirement.
Address Verification - Necessary to complete the CDD process
The customer identification process is incomplete unless sufficient details about the customer’s location are sought. And merely collecting the customer’s address is not enough. The regulated entities have to ensure that this address exists for real.
The following encounters in the course of the address verification process boost the regulated entity’s confidence in the customer’s identity:
- That the customer is cooperative and shared the required details and documents
- The documents and information related to the provided address are correct and genuine
- Information available to communicate with the customer
With the satisfactory conclusion of the address verification process, the regulated entity can make an informed decision about the customer’s onboarding.
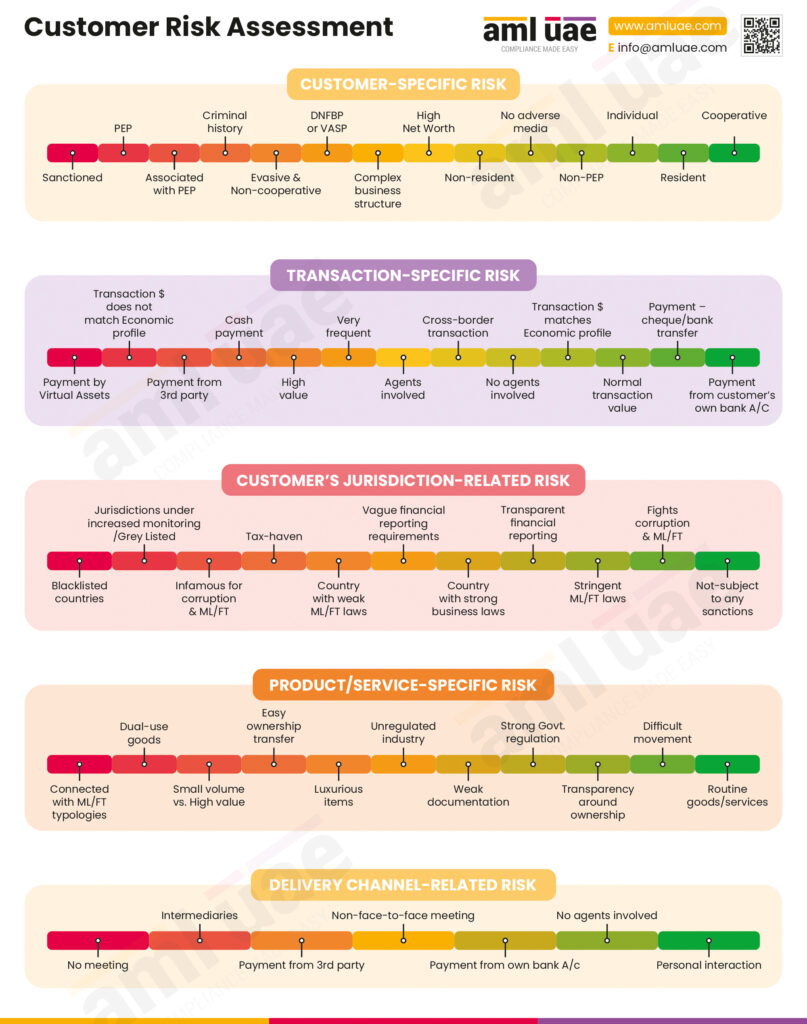
With adequate information about the customer’s location, the entity can spot any potential unusual customer activities, indicating attempts to launder the money or carry out any other financial crime. The risk indicators associated with address can be:
- The location of the customer and the regulated entity does not make sense (e.g., too far from the customer’s origin)
- Customer’s connection with high-risk jurisdictions
- Same address disclosed as correspondence address by multiple customers
- Frequent change in the customer’s address (e.g., customer declaring different addresses at the time of each transaction)
- Mismatch in the customer’s profile and the address provided (e.g., the customer holds nationality of country A, is working in country B, and the correspondence address offered is of country C)
- Discrepancies between geolocation and the IP address associated with the transaction
Further, the address verification process also helps gauge the customer’s possible association with any suspicious activity or terrorist and, thus, enables the regulated entity to carry out customer risk profiling sufficiently.
Consequences of inadequate Address Verification process
When the address verification process is not carried out thoroughly, the regulated entities may unknowingly and unwillingly onboard the fraudsters and financial criminals, trying to penetrate the systems under cover of fake identities. This may open up a platform for criminals to exploit legitimate businesses.
Further, without adequate address verification, the customer risk assessment could have been done with incorrect details (imaginary address provided by the customer), the outcome of which may not be reliable. This may lead to classifying the high-risk customer as low, leading to short due diligence measures being applied to the high-risk posing customer. The incorrect risk profiling also adversely impacts the regulated entity’s ongoing monitoring program, causing unwarranted hiccups in detecting and reporting suspicious transactions.
It does not end here. The address verification is also a regulatory mandate imposed upon the entities as part of AML measures. The regulated entities failing to develop and implement an intense address verification process would be subject to regulatory non-compliance fines. Further, failure to comply with the legal obligations may severely affect the entity’s reputation, leading to a loss of customers’ trust and authorities’ confidence in the business.
It is important to understand that inadequacies in even one of the AML measures can jeopardize the entire efforts made towards compliance. With a flawed address verification process, the customer identification measures would be ineffective, and the risk assessed inaccurate, paving the way for criminals to slip in and hamper the integrity and security of the financial system.
Navigating the right approach to the Address Verification process
Adopting a systematic approach to address verification empowers the entities to develop a holistic customer profile, which is necessary to spot anomalies.
An address verification exercise must involve the following steps to ensure the accuracy of the process and yield the desired results of thoroughly concluding the CDD process:
– Firstly, the regulated entities must obtain the customer’s address details. This includes information about the customer’s residence and business place. In case the customer’s present and permanent address differs, the regulated entity must obtain information about both, as this may impact the invalid assessment of the geographic risk arising from the business relationship.
To ensure the collection of complete details, the entity may have predefined fields in the “Know Your Customer” form, requesting the customer to provide the complete address, including PIN or Postal Code, P. O. Box No., etc., as applicable.
– Having collected the details, the regulated entity must verify the legitimacy of these details using reliable data to confirm that the place exists for real. This may include obtaining a recent utility bill, valid tenancy contract or other documents bearing the customer’s address like the bank statement or the municipal tax records. It is important to note that if reliance is placed on the utility bill or similar documents for checking the authenticity of the provided address, such documents must not be older than three months from the date of carrying out the address verification task.
Additionally, regulated entities like financial institutions may also resort to an alternative approach to verify the customer’s declared address, that is, through using postal services. This can be done by sending some customer’s account-related documents to the given address. If the given documents get delivered, the verification process may be deemed to have been concluded satisfactorily.
In the case of online or virtual transactions, the customer’s IP address must be mapped with the customer’s declared geolocation to rule out any possibility of suspicious activity.
– Maintaining the customer’s address details up-to-date is an essential aspect of AML measures. The regulated entity must ensure the customer database captures the relevant and current address. If there is any change in the address, the revised information and the corresponding documents to corroborate the same must be sought.
– Moreover, to bring effectiveness in the overall Customer Due Diligence process, the address must be mapped with the other identification details of the customer to draw a reasonable nexus between the two and identify if any irregularities exist.
When the address verification process is followed systematically, it complements the entity’s overall AML measures. It enables the regulated entities to adequately assess the customer risk and identify suspicious transactions while adhering to the AML regulations.

AML UAE – Your partner in combating the financial crime
The regulated entities must develop a customized AML program covering an effective and robust Customer Due Diligence process. And to help you with this, here is your one-stop AML solution provider – AML UAE. We help the regulated entities assess the business risk and design the CDD framework, highlighting the fundamental elements necessary to complete the customer identification and verification process.
Make significant progress in your fight against financial crimes,
With the best consulting support from AML UAE.
Our recent blogs
side bar form
Share via :
About the Author
Jyoti Maheshwari
CAMS, ACA
Jyoti has over 6 years of hands-on experience in regulatory compliance, policymaking, risk management, technology consultancy, and implementation. She holds vast experience with Anti-Money Laundering rules and regulations and helps companies deploy adequate mitigation measures and comply with legal requirements. Jyoti has been instrumental in optimizing business processes, documenting business requirements, preparing FRD, BRD, and SRS, and implementing IT solutions.
