Money laundering is all about hiding the source and nature of the illicit funds to make them appear as if they were obtained from some legitimate activities. The process of money laundering begins with the aim of disguising the original source of the criminal proceeds, and to do so, the illegal funds must be introduced first in the open economy. Placement is the first stage of money laundering where criminals use various methods like gambling, blending of funds, currency smuggling, etc., to introduce proceeds of crime into financial system.
What is Placement in Money Laundering?
A person who has received some ill-gotten gains will surely be on the lookout for measures to clean them in order to use them freely without any stipulations from regulators. So in order to use the funds, the criminal needs to disguise the source of proceeds to appear as the funds to be legitimate.
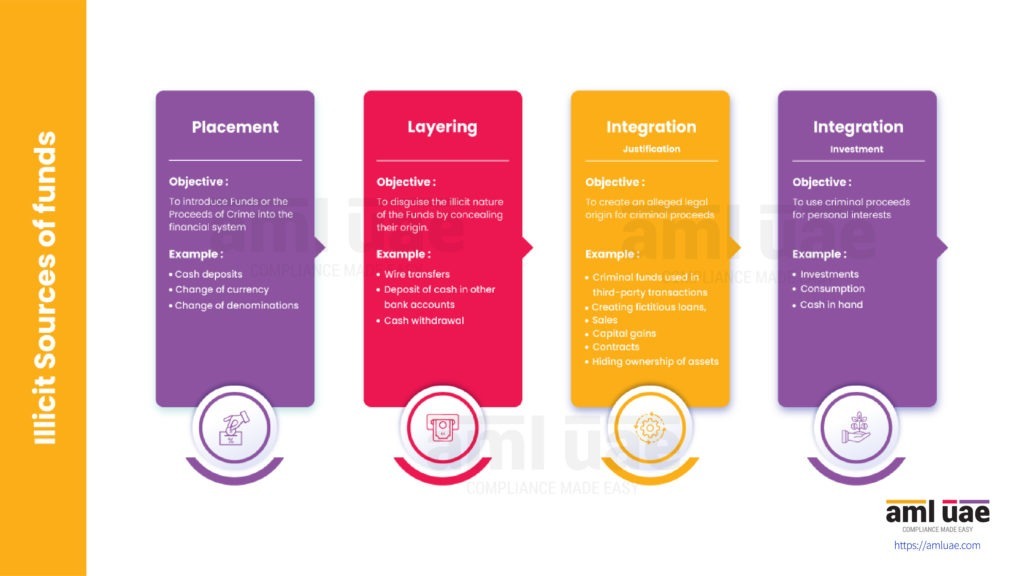
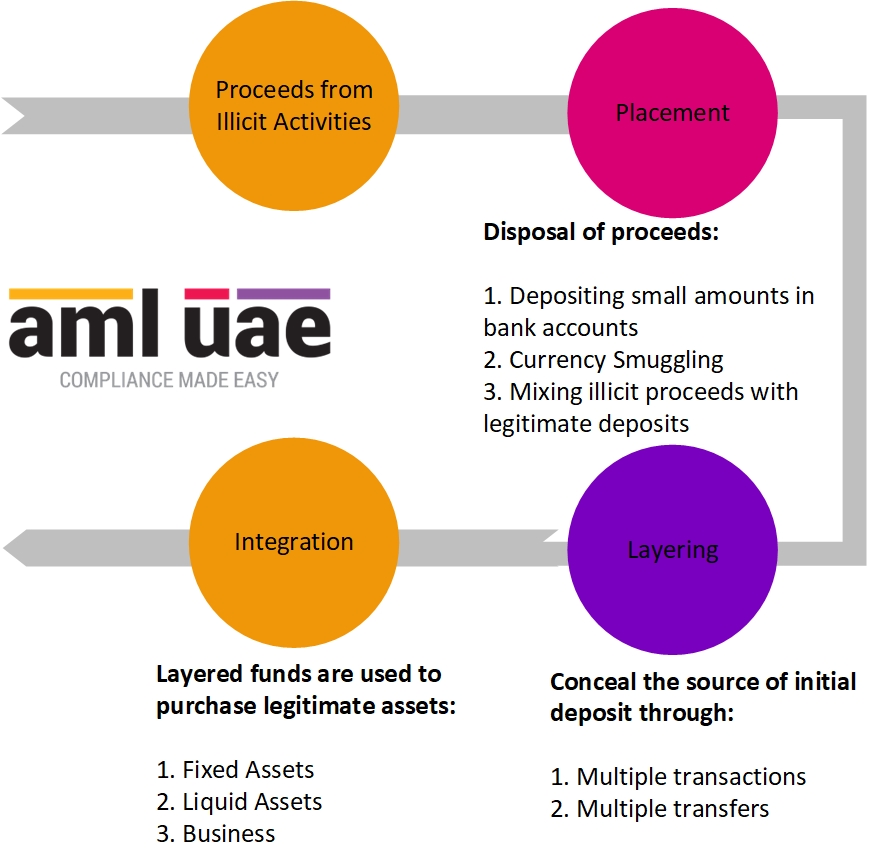
Money laundering involves a series of transactions to make its detection as difficult as possible. However, money laundering can broadly be classified into three stages. 1. Placement, 2. Layering, and 3. Integration. The placement stage of money laundering involves the physical introduction of cash or other assets derived from criminal activity into the financial system. Criminals use various placement techniques like structuring, blending of funds, currency smuggling, etc., to commit money laundering.
Definition of Placement in Money Laundering
Placement is the first stage of money laundering, where dirty money is introduced into the financial system. It is the most vulnerable stage, and the chances of a criminal getting caught are the highest.
The goal of Placement in Money Laundering:
- To hide the source of illicit money
- To distance the money from its illegitimate source
- To introduce dirty money into the financial system
The crimes like corruption, fraud, bribery, kidnapping, illegal arms trade, drug trafficking, smuggling, etc., are committed for money. Criminals obtain illegal proceeds, and then they try to find a way for their disposal without attracting the eyes of law enforcement.
Stages of Money Laundering
First: Placement Stage
The money launderer puts unlawful funds into circulation by depositing cash into the bank, executing any transactions to buy any luxury goods or using them in other legitimate businesses. This is the stage where the money launderer gets rid of illegal proceeds by placing them into the legitimate financial system.
The placement stage of money laundering is the most challenging for the launderer as the disposal of illegal proceeds by introducing them into the financial system causes suspicion.
Second: Layering Stage
Layering is the second stage of the three-step process. Under layering, the launderers make numerous transactions to distance the true owner and the source of illegal money, making it harder for the authorities to track. This can typically be as easy as using illegitimate funds to invest in something legitimate so that the funds now appear to be “clean”. Such funds are then transferred to purchase goods and services, making their detection nearly impossible.
Third: Integration Stage
Integration is the final stage of the money-laundering process. It is the stage where the disguised criminal proceeds are returned to and used by the money launderer, with a legitimate appearance given to the criminal proceeds.
When it comes to terrorist financing, integration is accomplished by distributing funds to terrorists and terrorist organizations.
Methods or Examples of placement in money laundering:
- Smuggling illegitimate cash or liquid monetary instruments.
- Blending unlawful proceeds with legitimate proceeds, such as illegitimate funds introduced into the cash-intensive grocery business.
- Repayment of debt using illegal proceeds.
- Buying stored value cards with illegitimate money.
- Depositing small amounts into several bank accounts to evade reporting threshold. It is also called smurfing, one of the most common money laundering techniques.
- Buying foreign currency with illegitimate funds.
- Cash purchase of a security or insurance.
- Invoice fraud – over-invoicing or under-invoicing.
However, it is not always the case that criminals resort to the placement stage of money laundering. Criminals can use illegal proceeds for various purposes without resorting to money laundering. Black money can be used to pay salaries to partners in crime, bribery, etc.
The placement stage of money laundering is only relevant if the criminals have to introduce money to the legitimate financial system. If the black money is going to be utilized for other criminal activities, then the placement of funds will not occur.
Businesses prone to the placement of illegal proceeds:
- Banks and Financial Institutions
- Insurance Companies
- Money Exchanges
- Capital Market
- Accountants
- Auditors
- Trust and Company Service Providers
- Lawyers
- Dealers in Precious Metals and Stones
- Virtual Asset Service Providers
- Casinos
- Art and antique dealers
- Restaurants
- Hotels
- Bars
- Nightclubs
- Vending machine operators
- Retail Businesses
- Luxury goods traders

Challenges and risks associated with Placement in Money Laundering
Since criminals use a variety of techniques in the placement stage of money laundering, its detection becomes a challenge for financial institutions and authorities. The AML/CFT laws and regulations require regulated entities to employ various control mechanisms to counter placement in money laundering. Placement has a negative impact on the global financial system as various cross-border financial crimes are committed to facilitate placement in money laundering. As per the UNODC report, the total amount of criminal proceeds generated in 2009, excluding those derived from tax evasion, may have been approximately $2.1 trillion, or 3.6 per cent of GDP in that year (2.3 to 5.5 per cent).
Risk Factors for criminals in the placement stage:
- Regulated entities consider large cash deposits as a red flag and submit a Suspicious Transaction Report (STR) with the FIU for further investigation.
- There are KYC and CDD requirements which require the customers to pass through the ID verification and Due Diligence checks. In high-risk situations, a source of funds and a source of wealth is required.
- Regulated entities perform increased scrutiny when they suspect money laundering or terrorist financing, as their goal is to counter illegal money entering the financial system.
Strategies for detecting and preventing placement in money laundering
Law enforcement agencies must keep themselves updated with the new money laundering typologies used by criminals to fight money laundering. The AML authorities need to detect money laundering crimes early to prevent them from getting too complex for their detection. The early detection of money laundering at the placement stage would save a country from harmful socio-economic impact.
AI helps institutions detect money laundering activities at the transactional level. AI systems tend to be simplistic and rule-based; a transaction will be flagged as suspicious and require a human-conducted review to determine if it fails to pass a set of rules outlined by the governing authorities. A proper set of AI tools can also minimize the rate of false positives.
The UAE government has significantly tightened measures for money laundering and financing of terrorism. Since it entered countries under increased monitoring set by global watchdog FATF, they have developed enhanced policies and guidelines for different sectors, especially where financial crime rates are relatively high.
How AML UAE can assist you in detecting and preventing of the placement of illegal funds?
AML UAE provides AML compliance services to Financial Institutions, Designated Non-Financial Businesses & Professions (DNFBPs) and Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) in the UAE.
AML UAE can assist you with performing your AML Business Risk Assessment to understand how your business can be exploited during the placement stage of money laundering and customizing the AML/CFT Policies, Procedures, and Controls to mitigate the risk, including imparting necessary training to effectively implement the AML framework.
Get in touch with us to remain compliant with the AML regulations in UAE.
Our Timely and Accurate AML consulting Services
For your smooth journey towards your goals
Our recent blogs
side bar form
Add a comment
Share via :
FAQs About Placement in Money Laundering
Placement is the first stage in which illegal proceeds are introduced into the legitimate financial system.
- Structuring and smurfing
- Wire transfer
- Insurance purchase
- Gambling
- Currency smuggling
- Currency exchange
- Blending funds
- Loan repayment
Structuring involves the execution of financial transactions in such a way that the placement of illegal proceeds from a crime does not trigger scrutiny by regulators and law enforcement agencies. Criminals deposit a small sum of cash into a bank to avoid the monetary threshold prescribed by the regulatory bodies.
Structuring and Smurfing are the terms used interchangeably, but they differ from each other. Structuring involves intentionally splitting a large financial transaction into a series of smaller transactions to avoid catching the eyeballs of regulators. Smurfing, however, includes structuring and using different accounts to deposit money into one or multiple financial institutions.
Placement is the first stage of money laundering. Here the black money from a crime is entered into a legitimate financial system.
Placement is the first stage of money laundering, where dirty money gets injected into the legitimate financial system. Layering is the second stage of money laundering, where the source of illegal money is concealed through a series of transactions.
Placement is the most vulnerable stage of money laundering for criminals, as placing large amounts of cash into the legitimate financial system may catch the eyeballs of law enforcement agencies.
Placement is the most vulnerable stage for money launderers as it’s the introduction of illicit funds for the first time into the system. So having an effective red flag indicators list will help mitigate the risks of money laundering in the initial stages itself.
The penalty for money laundering, if found guilty, is: Not more than 10 years and a fine between 100,000 AED to 5,000,000 AED or either one of these.
The illegitimate funds, obtained through some criminal activities need to be placed initially into the financial system to commence the money-laundering process. The process of putting the criminal proceeds into the legit financial system is construed as the “placement” stage, from where the money laundering activity begins.
Some common methods used for placement in money laundering.
- Smuggling illegitimate cash or liquid monetary instruments.
- Mixing unlawful funds with legal business activities.
- Repayment of the loan using illegal funds.
- Buying stored value cards (Debit cards) with illicit money.
Placement is the most vulnerable stage for money launderers as it’s the introduction of illicit funds for the first time into the system. So having an effective red flag indicator will help identify and mitigate the risks money laundering in the very beginning itself.
Yes, several industries are prone to money laundering, especially in the placement stage:
- Money Exchanges
- Banks
- Capital Market
- Trust and Company Service Providers
- Lawyers
- Dealers in Precious Metals and Stones
- Virtual Asset Service Providers
- Casinos
- Art and antique dealers
The money laundering process begins with the placement stage, wherein the proceeds of financial crime are placed into the legitimate economy.
The act of depositing illicit money in a financial institution corresponds with the placement stage of money laundering.
About the Author
Pathik Shah
FCA, CAMS, CISA, CS, DISA (ICAI), FAFP (ICAI)
Pathik is a Chartered Accountant with more than 25 years of experience in compliance management, Anti-Money Laundering, tax consultancy, risk management, accounting, system audits, IT consultancy, and digital marketing.
He has extensive knowledge of local and international Anti-Money Laundering rules and regulations. He helps companies with end-to-end AML compliance services, from understanding the AML business-specific risk to implementing the robust AML Compliance framework.



