Video on Enhanced Due Diligence as part of the AML Program
Video on Enhanced Due Diligence as part of the AML Program
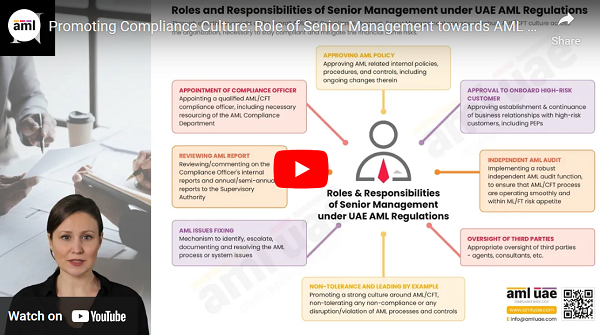
The regulated entities, such as DNFBPs, Financial Institutions, and VASPs, are required by the UAE AML Regulations to evaluate the risk that each customer poses to the company and implement Enhanced Due Diligence procedures to manage high-risk customers.
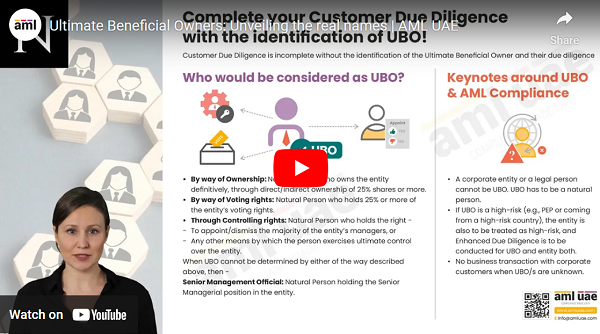
EDD involves investigating the customer’s identity in depth, whether legal or personal. It also involves inquiring into the customer’s wealth and funding sources and verifying their legitimacy.
EDD allows the regulated entity to distinguish between customers who are simply posing an increased risk and customers who are actually suspected of being connected to financial crime through additional checks.
The regulated entities can protect their reputation by avoiding doing business with consumers who are connected to illegal activities. One of the EDD strategies is getting top management’s consent when working with high-risk customers to ensure that management understands and approves of the heightened risk.
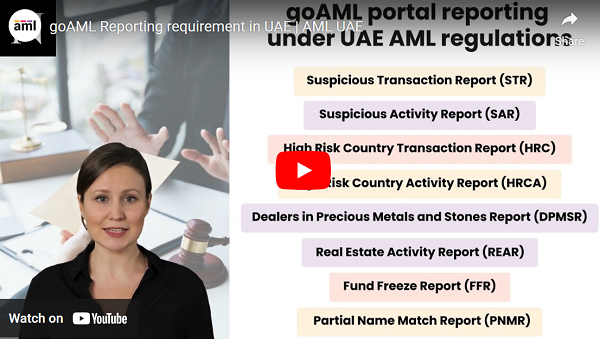
Finding any third parties engaged in the transactions with bad intentions is made easier for the regulated entities by EDD. EDD enables the regulated company to safeguard its operations against possible risks and dangers while also helping it comply with regulatory reporting obligations.
Chapters:
- 0:00 Introduction on Understanding the importance of Enhanced Due Diligence as part of the AML Program
- 0:47 How EDD helps to determine the purpose behind the complex business structure?
- 1:18 How to determine the legitimacy of SOF and SOW?
- 1:49 How to distinguish between suspicious customer and non-suspicious customer?
- 2:23 What is retaining brand image?
- 2:46 Why making informed decisions is necessary in EDD?
- 3:14 How EDD ensure that no-third party is involved?
- 3:39 How EDD helps in meeting regulatory requirements?
- 4:03 Conclusion and regards
Related Infographics
Related Articles
Related Videos
Related eBooks:
Share via :
Our recent downloads
side bar form
Share via :