Role of an Auditor Under UAE AML Compliance
The UAE has implemented anti-money laundering laws and ensures strict compliance to help fight this rampant financial crime. The objective of the AML laws is to get rid of money laundering and prevent large-scale funding of criminal and terrorist financing. Banks, financial institutions, DNFBPs – Designated Non- Financial Businesses & Professions, and other regulated entities must follow the AML rules. The role of an auditor under UAE AML Compliance is massive. The auditors act as guardians who ensure that the organizations adhere to the compliance rules and do not leave any scope of non-compliance.

The AML law was implemented by Cabinet Decision No. (10) of 2019, Federal Decree No. (20) of 2018. It strengthens the AML compliance network and has strengthened UAE’s AML/CFT legal and institutional framework per the FATF recommendations.
The auditors analyse the nature of the business and their obligations in the context of the UAE Anti-Money Laundering Laws. Every business is unique, so they examine the accounts, documents, control policies to identify suspicious transactions and doubtful accounts with great vigilance.
What is the role of an auditor under UAE AML Compliance?
There are several duties of an auditor that are performed to prevent money laundering, which has serious financial repercussions on the country’s economic structure and the world economy at large. The duties of an auditor can be defined as follows:
- Examination of annual records and accounts.
- Analyse the internal control procedures.
- Identifying any suspicious transaction and taking the appropriate action to prevent money laundering.
- Assessment of money laundering risk and evaluating transactions to detect financial terrorism.
- Compliance- to check whether the institution complies with rules and regulations laid down by the authorities.
- Prevent the clients from AML violation risks by evaluating risks on two parameters-
(a) Assessment of own risk regarding the nature and type of the business.
(b) Obligation of risk assessment when appointed to carry out the auditing duties.
Auditors perform various duties such as conducting the valuation of the assets and liabilities, approving bad debts, etc. They receive compensation for their duties, and they need to consider other risks that involve service risks, customer risks, location risks, etc.

Critical factors for consideration include:
- Nature and the type of business.
- Nature and volume of the financial transactions. Country’s origin of the interested or associated parties and determine whether they belong to a high-risk country.
- Communication channels with which clients are introduced.
Auditors provide their valuable opinion on the transactions that might be associated with money laundering. They will provide their expert opinion on the valuation of the assets and liabilities, approval of mergers and acquisitions or approval of writing off bad debts, etc. The auditors review the internal policies, procedures, and controls. They provide their expertise in appointment compliance officers and ensure that the company adheres to rules and regulations and prevents violation of AML laws. They check the background verification system of CDD using different methods based on the business type, nature, and size.
Carry out the CDD process
Auditors conduct the Customer Diligence process and follow a strict risk assessment process to evaluate the risk of the company’s AML compliance and those of its clients. The auditors use various resources and ensure that the company they associate with has a clean record. They need to be unbiased in their observation and documentation process to have a clear picture of customer due diligence.
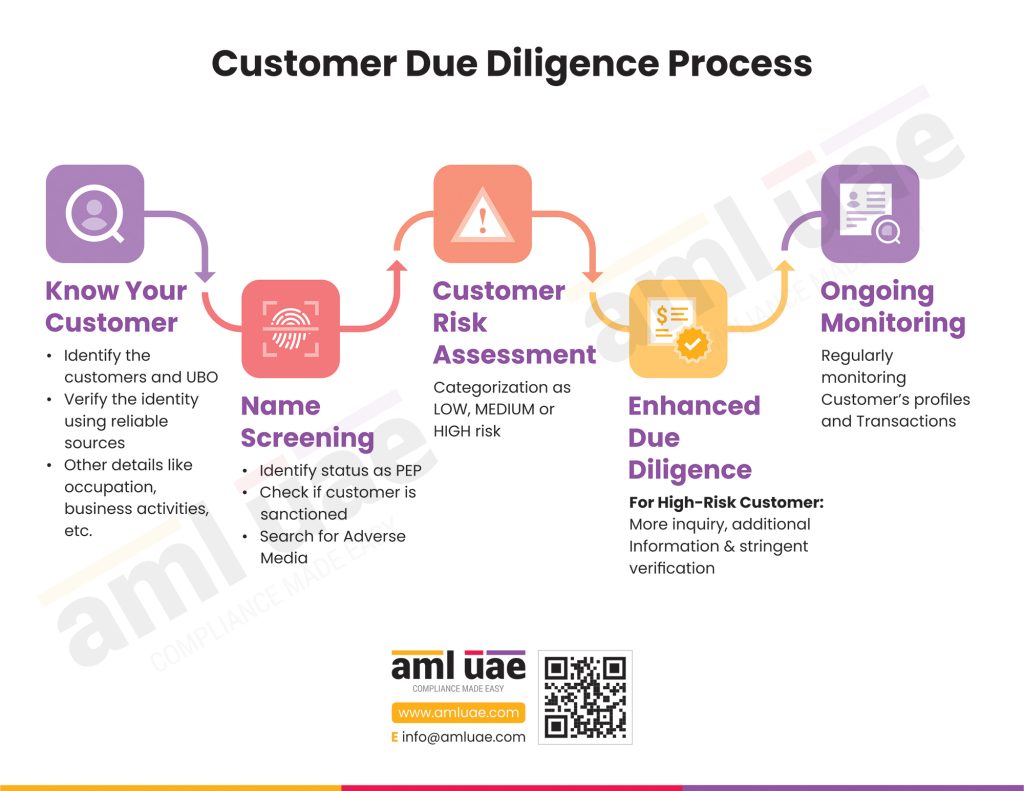
Identifying suspicious transactions and reporting the same to the respective authorities.
Auditors need to keep a vigilant eye on the transactions of the clients. If they find any transaction suspicious and have a reasonable ground for doing so, they have to report the case to the Financial Intelligence Unit using the goAML Portal.

How can AML UAE assist you?
AML UAE is one of the most reputed AML consultants serving thousands of businesses in the UAE and offering robust support in AML compliance. Our panel consists of AML compliance consultants with in-depth knowledge of the UAE AML rules and regulations. Get a risk-based approach for annual AML report filing services. We assist DNFBPs in complying with the AML requirements. To obtain further detailed information about this reputed consultant, feel free to visit AML UAE.
Our recent blogs
side bar form
FAQs on Role of an Auditor
The auditor must perform the following duties under AML Law:
- Examine and evaluate AML policy, controls, and procedures to ensure compliance with the law.
- Make necessary recommendations in relation to AML policy, controls, and procedures.
- Check if those recommendations have been taken into consideration by the management and complied with.
Add a comment
Share via :
About the Author
Pathik Shah
FCA, CAMS, CISA, CS, DISA (ICAI), FAFP (ICAI)
Pathik is a Chartered Accountant with more than 25 years of experience in compliance management, Anti-Money Laundering, tax consultancy, risk management, accounting, system audits, IT consultancy, and digital marketing.
He has extensive knowledge of local and international Anti-Money Laundering rules and regulations. He helps companies with end-to-end AML compliance services, from understanding the AML business-specific risk to implementing the robust AML Compliance framework.



