Right AML Solution to foster Corporate Service Providers’ AML Function
With emerging financial crime typologies and ever-changing regulatory requirements, the regulated entities, including the Corporate Service Providers, need robust AML software to mitigate the risk and stay AML compliant.
Corporate Service Providers are vulnerable to financial crime as they offer services like the formation of legal structures or legal arrangements, providing nominee services, assistance in the administration of trusts or special asset protection vehicles, etc., which may be exploited by the money launderers or other criminals to move their illegal proceeds.
By designing and implementing a comprehensive set of AML measures, backed by deploying the right technology and tools, the Corporate Service Providers can timely identify and prevent money laundering and terrorist financing risks and ensure compliance with the UAE AML regulations.
With this article, let us explore the key points to be considered and the step-by-step approach to selecting the right AML software to enable a Corporate Services Provider (CSP) to adhere to the UAE AML regulations and avoid non-compliance consequences.
AML Compliance Software’s Capabilities to be looked for by the CSP
When searching for an AML software or system, the CSP must consider the AML compliance obligations imposed under UAE AML regulations and the capabilities of the solution to support the same:
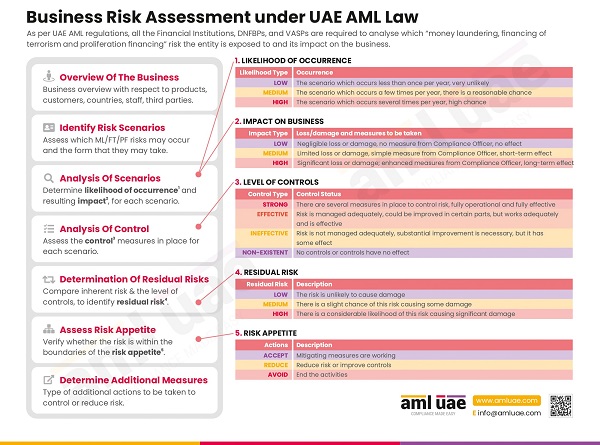
Assessing the business risk
As conducting an Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessment helps the CSP evaluate the ML/FT risks and customize the AML program, the CSPs shall look for a solution to assess the business risk. The functionality must be comprehensive, enabling risk assessment considering the relevant risk parameters such as the type and activities of the customers, the location of business operations, the nature of transactions and the services offered, etc.
Assessing risk just once is not enough; the solution should adopt a dynamic approach to risk assessment, wherein the outcome of EWRA is updated as and when the CSP’s risk factor significantly changes.
Streamlining the Customer Due Diligence Process
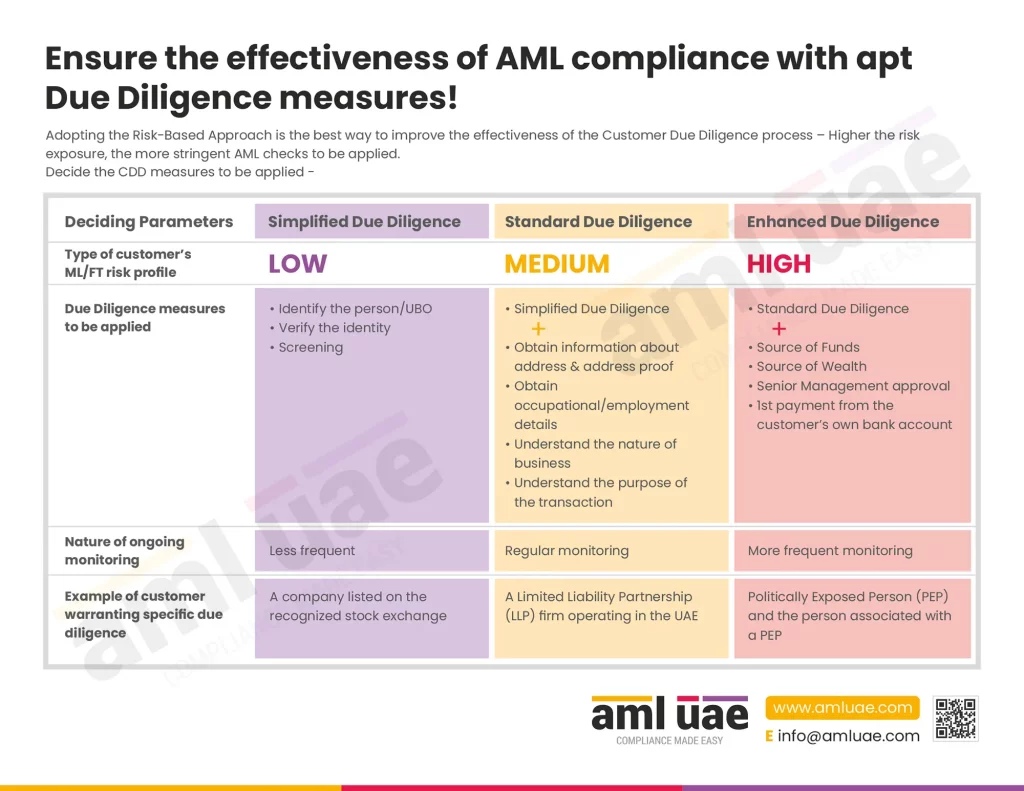
The CSPs in UAE are required to implement a robust Customer Due Diligence (CDD) process to identify the customers, determine their risk levels, and apply adequate mitigation measures.
Hence, the AML solution must support the CSP in navigating the CDD steps smoothly, which includes the following:
- Capabilities for customer identification and verification of their identities, whether it is an individual or a corporate customer,
- Screening the customers against the Sanctions Lists (specifically UAE Local Terrorist List, UNSC Consolidated List, and facility to configure other international lists relevant to the CSP’s operations),
- Screening the customer to identify any nexus with a Politically Exposed Person (PEP) or has any adverse or negative media against the person,
- Conducting customer risk assessment considering their identification details, the outcome of screening, etc., to determine the risk profile.
Continuous Monitoring of Business Relationships and Transactions
The customer’s profile may change in the course of the business relationship. Thus, the solution must support the ongoing monitoring of the customer’s information, time flagging off the expiry of the identity documents, change in the customer’s PEP status or screening outcome, etc.
Further, ongoing monitoring of transactions is also very critical for CSP to track the customer’s activities and their consistency with the initially assessed risk category. With technological support, the CSPs can easily monitor large volumes of data, develop a pattern to identify suspicion or unusual activities and generate timely alerts to prevent and report such matters to FIU.
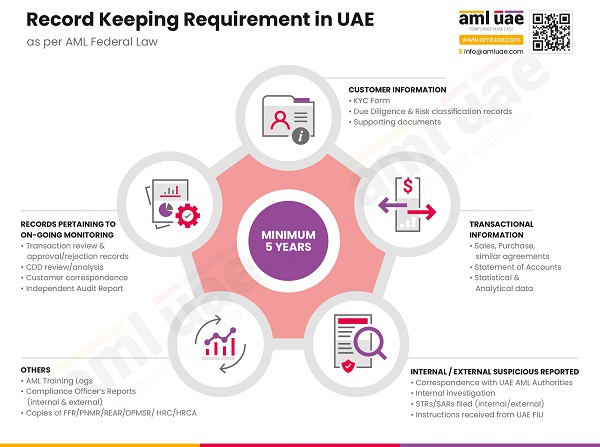
Record Keeping and Reporting Capabilities
The solution must also have robust document maintenance and reporting functionalities. The documents and data uploaded on the solution must be maintained in an organized manner and shall be readily accessible. The software must allow the CSP to generate and analyze the reports on customers, transactions, risk profiles, suspicion or red flags observed, etc.
Further, the customization capabilities must be available to configure the reporting requirements to support the CSP’s Compliance Officer in meeting the regulatory obligations.
Integrating with the CSP’s Existing Business Solution
The potential of the AML solution can be optimally utilized when the same is integrated with the business solution that the CSP is using. The AML tool must seamlessly connect with the existing IT infrastructure for a smooth exchange of data around customers and transactions, reducing the redundant efforts or delicacy of the data, streamlining customer onboarding, and making identifying red flags easy and prompt.
User-Friendly Navigation
The AML system must be easy to interact and use, ensuring that the team can effectively utilize the functionalities without much investment in training, and a comprehensive User Manual can be enough to explore basic features. The solution’s functionalities must be logically placed, allowing users to access the required items. Further, a “Help Kit” must be available, which the users can refer to and resolve any technical or contextual aspect of using the solution.
Right approach to select the right AML Compliance Solution
Having discussed the functions and capabilities to look for in an AML solution, let us discuss the selection process. There is many software available in the market offering the same set of features. In such cases, identifying an appropriate AML software is in itself an art requiring a lot of deliberations of various factors, as once you invest in the software, you may expect to continue using it for the longer future and not spend your resources on frequently switches from one to another tool.
So, identification of the right software must be done using a systematic approach, as detailed under:

Assessing the AML Compliance requirements and Preparing the Business Requirements Document (BRD)
The CSP must first understand the business-specific AML compliance obligations in the context of the nature of services offered, the geographies the CSP deals with, the size and complexities of the transactions, etc. This understanding must be mapped with the features required in the AML solution. This Business Requirement Document (BRD) must cover the functional and non-functional aspects of the software the CSP is expecting, including the need for configurable parameters and customization possibilities. Further, this BRD must be approved by the CSP’s senior management, bringing them onboard concerning the required features and the budget allotted.
This BRD shall serve as a base and assist the CSP in navigating the software selection process.
Identifying and shortlisting a few AML solution providers
The CSP’s Compliance Officer must look for options matching the requirements. While identifying the software vendors, the CSP must consider the following factors:
- Functionalities available
- Pricing of the product, including any hidden or contingent costs
- Reputation of the software provider (looking for customer reviews, testimonials, etc.)
- Vendor’s readiness to handhold and train the team initially
- Vendor’s post-implementation support
- Scalability of the solution
Considering these parameters, the CSP must shortlist 2-3 solution providers that best match the AML compliance requirements and fit within the CSP’s budget.
Arrange for the demonstration of the solution
Once the potential fits have been identified, the CSP must arrange for a demonstration of these solutions to have a look and feel of the features offered and test the capabilities. Practically accessing the software and interacting with the vendor will give an understanding of the user interface, customization possibilities, vendor’s commitment towards training and after-sale services, etc. On the basis of this understanding, the CSP must score each of the shortlisted solutions, consider the pros and cons, and finally decide which one to go ahead with.
Get it started with proper documentation
Once the right software is identified, the CSP’s Compliance Officer must involve senior management and seek their support in closing the agreement. The agreement must be worded, specifying the scope of the parties, the features support, the prices, duration, any additional charges that may be levied in the future, etc.
As the AML software is a breakthrough for implementing the AML program, the choice of software must be made wisely following the proper decision-making methodology; otherwise, it can bring you reputation loss and non-compliance penalties.
Let AML UAE assist the Corporate Service Providers strengthen their AML Function with the right AML tool!
Deploying the right software is critical for Corporate Service Providers in the UAE to ensure timely compliance with regulatory obligations, identify financial crime risks, and prevent and report the same. Let experts assist you in this process.
AML UAE is a leading AML consultancy firm, providing end-to-end AML support to the regulated entities in UAE, including Corporate Service Providers. With our understanding of the regulations, we can assist you in defining your AML compliance requirements, preparing a detailed BRD, and identifying the right fit for your compliance needs. We do not stop here; we ensure that the solution implementation is a smooth ride for you without bothering your routine business activities, but at the same time, meeting your ongoing AML compliance requirements.
Make significant progress in your fight against financial crimes,
With the best consulting support from AML UAE.
Our recent blogs
side bar form
Share via :
About the Author
Jyoti Maheshwari
CAMS, ACA
Jyoti has over 6 years of hands-on experience in regulatory compliance, policymaking, risk management, technology consultancy, and implementation. She holds vast experience with Anti-Money Laundering rules and regulations and helps companies deploy adequate mitigation measures and comply with legal requirements. Jyoti has been instrumental in optimizing business processes, documenting business requirements, preparing FRD, BRD, and SRS, and implementing IT solutions.
