Understanding the Difference between UAE Federal AML Law and DIFC AML Rulebook
Understanding the Difference between UAE Federal AML Law and DIFC AML Rulebook
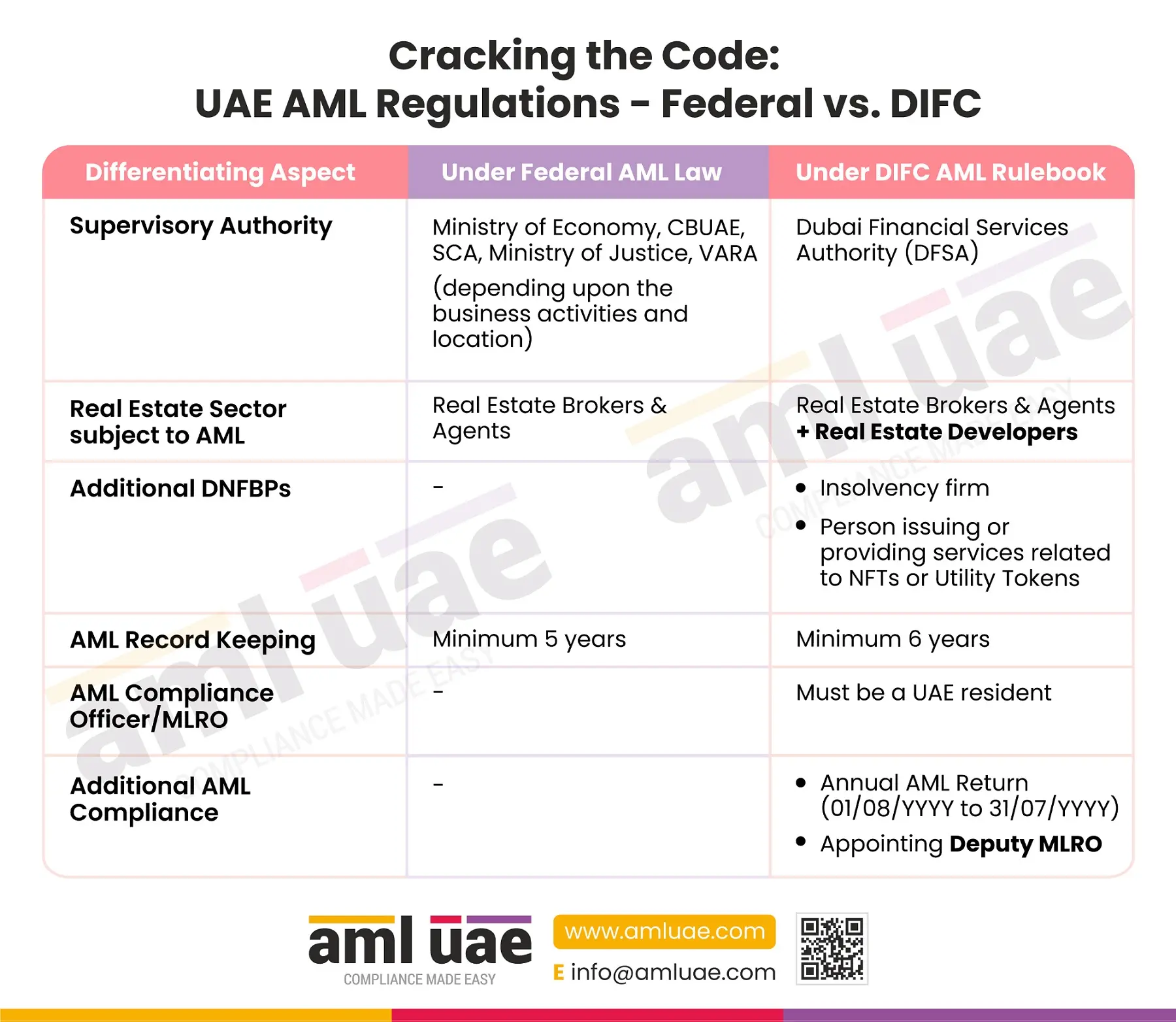
The regulated entities operating in the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) are required to comply with the DFSA-issued AML Rulebook, along with the AML Federal Decree-Law and the corresponding Cabinet Decision. Though the DIFC AML Rulebook is developed in line with the Federal AML regulations, there are a few differences between the two, which the DFSA-regulated entities must take into consideration.
The above-mentioned infographic distinguishes the following AML provisions under the Federal Law and the DIFC AML Rulebook:
1. One of the differences, indirectly mentioned above, is related to the Supervisory Authority. The DIFC-based entities are subject to AML supervision by the DFSA – Dubai Financial Service Authority. While, the mainland companies subject to Federal AML regulations vary based on the nature of operations – such as the Central Bank of UAE for Financial Institutions, Ministry of Economy for the Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs), and Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA) for Dubai-based Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs).
2. With respect to the real estate sector, only real estate brokers and agents are subject to AML compliance as per Federal Law. However, the DIFC AML Rulebook extends the compliance regime to the DIFC-based real estate developers as well.
3. Moreover, the following two classes of activities or professions are additionally covered under the definition of “Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions” (DNFBPs) under the DIFC AML Rulebook:
- Insolvency firms
- Person engaged in the issuance of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTS) or utility tokens or providing related services.
4. The AML documentation requirement is for a minimum period of 6 years in DIFC, as compared to a minimum of 5 years under Federal AML Law.
5. The DIFC AML Rulebook mandates that regulated entities have a UAE resident as an AML Compliance Officer or Money Laundering Reporting Officer (MLRO). There is no such requirement under Federal AML Laws.
6. In addition to the AML compliance obligations imposed under Federal AML Laws, the DIFC entities are required to comply with the following two AML requirements:
- Filing an AML Annual Return with the DFSA (for the period starting from August of the previous year till July of the year in which reporting is to be done) and
- Appointing a Deputy (MLRO) to manage the AML program in the absence of MLRO.
Ensuring compliance with the DIFC AML Rulebook is very crucial for the regulated entities operating in or from the DIFC.
Let AML UAE be your handholding partner, guiding you throughout the AML compliance journey. With our experience in Federal AML Laws and the DIFC AML Rulebook, we can assist your business in customizing the AML program to stay regulatory compliant and safe against ML/FT vulnerabilities.
UAE Federal Laws vs DIFC Rule Book: Related Resources and Insights
Related Infographics
- AML Supervisory Authorities in UAE
- UAE’s 12 Strategic goals related to AML and CFT
- Reporting on goAML Portal under UAE AML Regulations
- Simplifying UAE FIU goAML Registration: A Visual Guide
- Role of AML Compliance Officer in UAE
- An illustrative list of factors for conducting AML Business Risk Assessment
- Filing of Fund Freeze Report (FFR)
- Filing of Partial Name Match Report (PNMR)
- When to file SAR under UAE AML Law
- When to file STR under UAE AML Law?
- Designing a comprehensive AML Training Program
- Responsibilities of Senior Management around the AML Program
- Elements of AML Compliance Officer’s Report to Senior Management under UAE AML Regulations
- Independent AML Audit
Related Videos
- AML/CFT Compliance Requirements in UAE
- Top videos on AML compliance: Defending against financial crime
- goAML Registration Step-by-Step Guide
- Role of an AML Compliance Officer under UAE AML Regulations
- AML Business Risk Assessment (BRA) and how to conduct BRA
- Factors for AML Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessment
- Elements of effective AML Policies and Procedures
- Know Your Customer process under UAE AML Regulations under AML UAE
- PEP and PEP Screening under UAE AML Regulations
- Decoding the types of Customer Due Diligence
- Mitigating high ML/FT risk with Enhanced Due Diligence
- Source of funds and source of wealth Essential element of Customer Due Diligence
- Sanctions Screening in UAE
- Differentiating Suspicious Activity vs. Suspicious Transaction
- Staying Ahead in AML Compliance: Understanding When to file STRs
- Defeating Financial Crime: Inside the AML Training Program
- Promoting Compliance Culture
Related Articles
- goAML Registration Guide
- What Skills Should an AML Compliance Officer Possess?
- AML Compliance Officer: Role and Responsibilities
- AML Risk Assessment before launch of a new product or service
- How to update the AML Policies, Procedures, and Controls in line with UAE AML Laws?
- A complete guide to effective customer due diligence
- AML Implications for Politically Exposed Person (PEP)
- Best practices for KYC compliance
- Customer Identification – A Critical Component of AML Compliance
- How to Detect High-risk Customers and Safeguard Your Business
- Guide to Enhanced Due Diligence
- Targeted Financial Sanctions (TFS): Legal Requirements in UAE
- The Challenges of The Sanction Screening Process
- Right AML Solution to foster CSP’s AML compliance
- Red Flag Indicators For AML/CFT
- Why is AML training critical for your employees?
- Importance of AML Training
- In-house AML Compliance Department Setup
- Why is Record-Keeping of Customer Identity and Transactions necessary?
Related eBooks:
Related Laws, Guidelines, Rules, and Regulations: