Navigating AML/CFT Challenges: Recognizing Common Typologies
Navigating AML/CFT Challenges: Recognizing Common Typologies
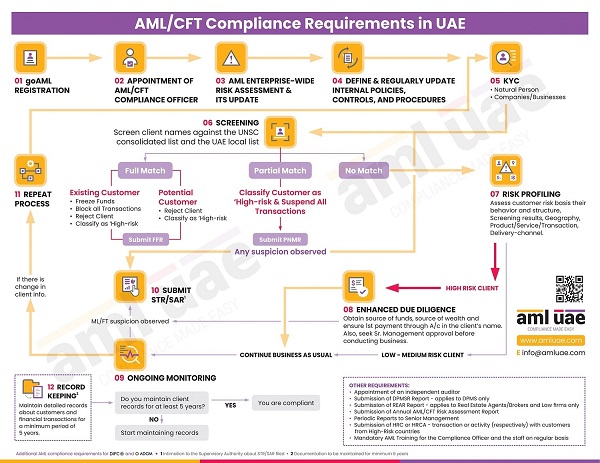
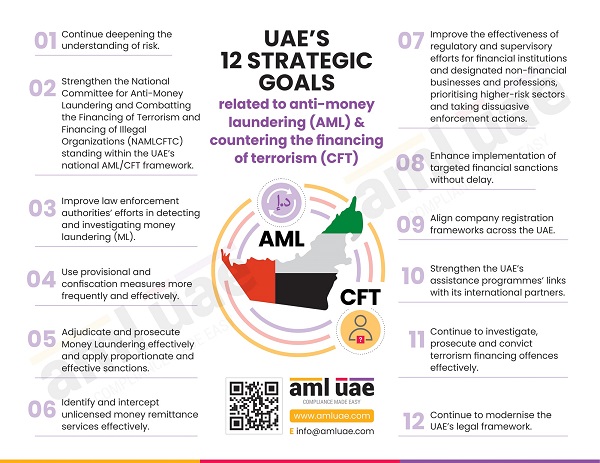
The Financial Institutions, Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs) and Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) must comply with AML regulations and develop a robust AML compliance framework dedicated to identifying and preventing money laundering, terrorism financing and other financial crimes. In this course of AML compliance and safeguarding the business, the entities must understand the ML/FT vulnerabilities associated with the nature of customers and products/services it deals with and stay alert to spot and curb these threats.
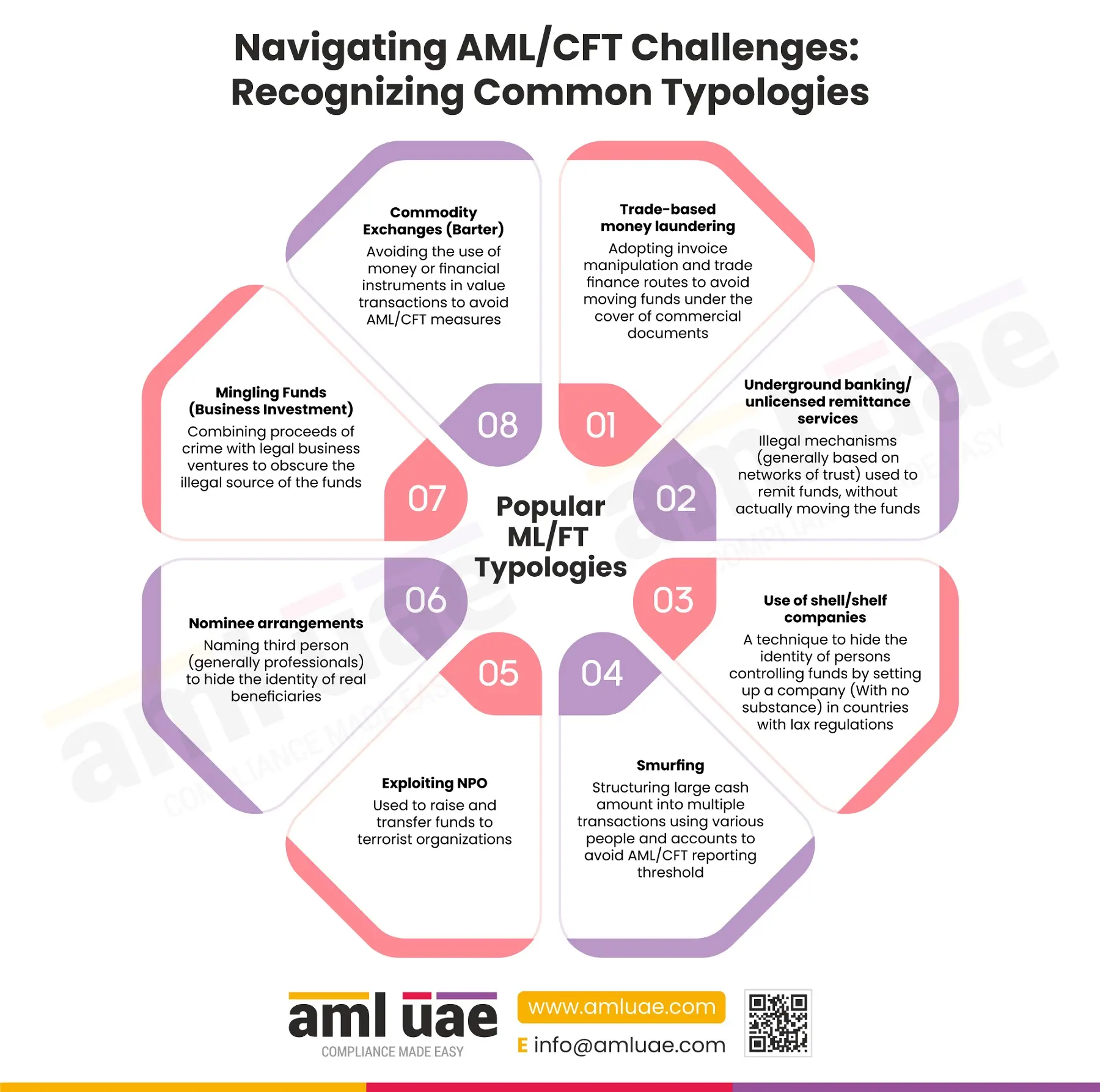
Some common ML/FT Typologies are:
- Trade-based money laundering: A money laundering technique used to transfer illicit money, disguising it in the name of commercial transactions. It includes over or under-invoicing, over or under-shipment, bogus shipping documents without actual delivery, etc.
- Underground banking/unlicensed remittance services: Illegal and informal mechanisms (generally based on networks of trust) used to remit funds without actually moving the funds. This is also known as “Hawala service provider”.
- Use of shell/shelf companies: A technique where legal structures are developed on paper, without any physical structure, employees or intent to carry out actual business activities. These entities are used to obscure the identity of the beneficial owners and move the criminal proceeds between the source and the shell structure, creating a complex web of transactions during the layering stage of money laundering.
- Smurfing: Smurfing is a structuring technique where a large cash amount is split into numerous smaller denominations – deposited in various accounts opened under different names to avoid any AML/CFT inquiries or reporting.
- Exploiting NPO: As per FATF evaluation, it is observed that NPOs are increasingly being misused to raise donations and transfer funds to terrorist organizations.
- Nominee arrangements: Here, some third parties (generally professionals like lawyers and company service providers) are named as the beneficial owners of the controlling parties on legal documentation to conceal the actual beneficial owners.
- Mingling Funds (Business Investment): During the integration stage of the money laundering process, the illicit funds are intentionally mingled with the legal business ventures to make separating legit and illegal funds difficult.
- Commodity Exchanges (Barter): Bartering the commodities is a standard ML/FT technique used to carry out transactions without touching the financial systems and, thus, apparently dodging the application of AML/CFT measures. For example, buying real estate property in exchange for diamonds and precious metals.
Here is an infographic discussing some of the widespread money laundering and terrorism financing-related typologies, which the regulated entities must consider and factor in while devising their AML compliance program.
AML UAE is here to help you understand these typologies and personalise the AML policies and procedures. We craft a comprehensive AML program for your business to ensure that you timely identify any ML/FT instances attempted through your business and take appropriate action to prevent and report the same.