Key Risk Indicators Linked to Customer Address Verification
Key Risk Indicators Linked to Customer Address Verification
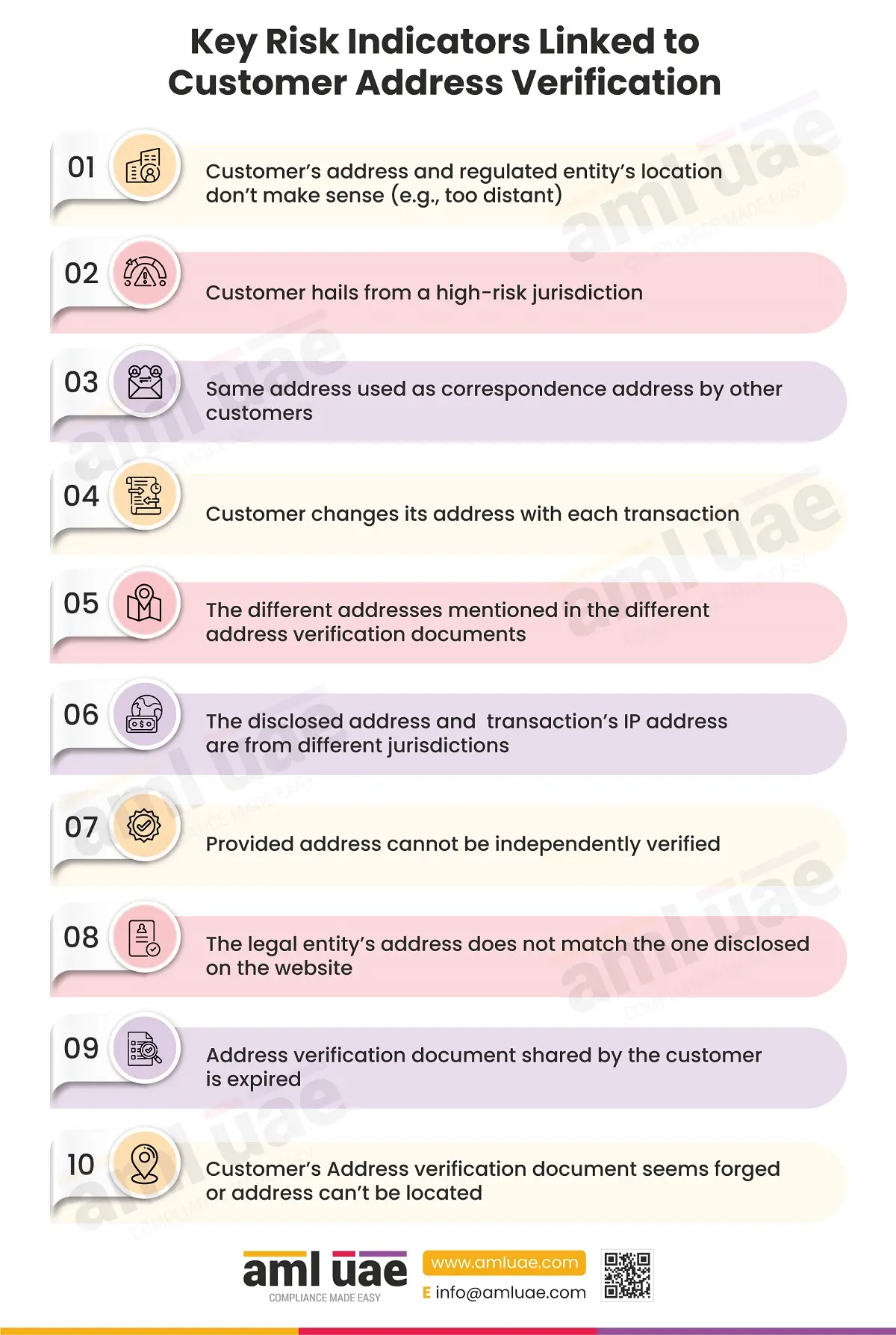
While conducting customer due diligence (CDD), one of the important steps is to Know Your Customer (KYC).
The KYC process requires the regulated entity to obtain details about the customer’s identity and place of residence or place of business, as the case may be. As part of KYC, the regulated entities must verify the address using a reliable, independent source (such as obtaining a valid copy of utility bills, bank statements, tenancy contracts, etc.). Address verification is one critical measure to establish the legitimacy of the customer’s identity and identify suspicious activities.
The address verification process is not restricted to learning about the customer’s address. The regulated entities need to make sure that the address truly belongs to the customer and exists for real. If the customer is cooperative and provides genuine information during the address verification, then the regulated entities can give it a green signal (if no other red flags are observed).
However, there are certain scenarios when the regulated entities need to be cautious and take action to mitigate the chances of the incorrect or fake addresses provided, obscuring the identity and indulging in financial crime. With this infographic, understand the key risk indicators associated with the customer address, which a regulated entity must be cautious of.