How to Detect High-risk Customer and Safeguard Your Business
Money laundering and terrorism financing are significant threats to the integrity of the global economy. Various countries have implemented regulatory anti-money laundering and combating of financing of terrorism (AML/CFT) frameworks, laying down detailed guidelines around how to detect high-risk customers and safeguard the business.
Similarly, UAE authorities have implemented the AML/CFT regulations covering Financial Institutions, Virtual Assets Service Providers (VASPs), and Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs). The UAE AML regulations mandate the regulated entities to conduct customer risk assessments to detect high-risk customers and apply Enhanced Due Diligence measures.
This article discusses the aspects to be considered for identifying high-risk customers and potentially suspicious activities and developing robust customer risk assessment frameworks.

Understanding AML compliance and high-risk customers
Before discussing the identification of high-risk customers, it is essential to understand why AML/CFT compliance is necessary and what customer characteristics would be considered high-risk from a money laundering perspective.
What is AML compliance?
Money laundering is a global problem adversely impacting the security and stability of society as a whole. Under money laundering activities, the financial criminals attempt to hide the source of the illegally obtained proceeds and disguise it to make it appear as though they were generated from legitimate economic activities. While through terrorism financing, the criminal provides financial assistance to propagate terrorist activities.
To fight these vices, there is a need for AML/CFT compliance. AML/CFT compliance is a set of measures implemented to identify and prevent money laundering and terrorism financing activities. The AML/CFT compliance includes developing robust internal policies and procedures to identify and verify the customers and monitor their activities to detect any unusual or suspicious behaviour.
AML compliance is mandatory for regulated organizations to safeguard their businesses against exploitation by financial criminals, avoid administrative penalties for regulatory non-compliance and ensure the integrity of the business. The failure to comply with AML regulations results in huge fines, legal actions against the business and irreversible damage to the reputation of the organization.
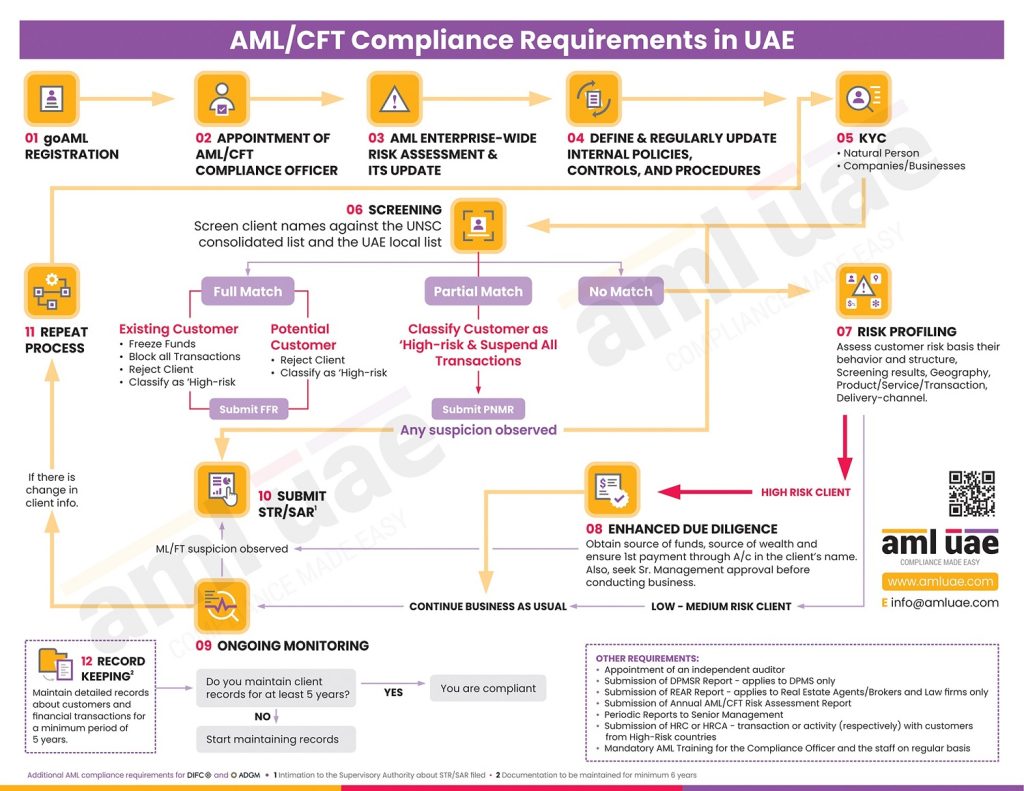
Who are considered high-risk customers under UAE AML regulations?
The customers posing increased ML/FT risk to the business would be construed as high-risk customers under the AML framework. The following would be construed as a high-risk customer from ML/FT perspective:
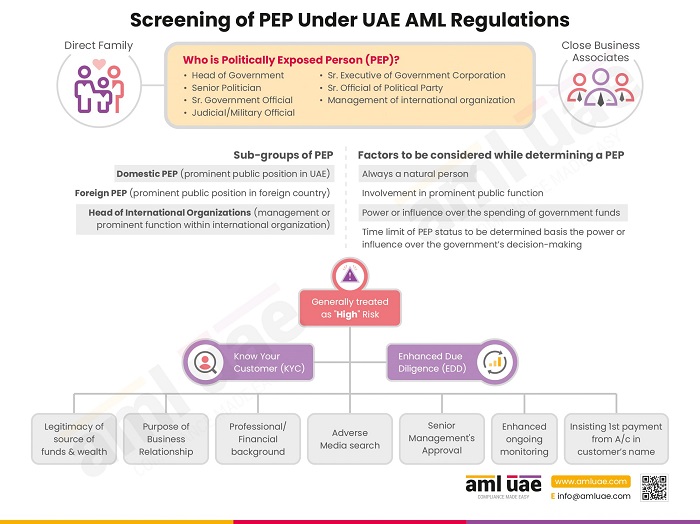
- Individuals who are Politically Exposed Persons (PEP) and the individual or legal person associated with PEPs
- The PEP is entrusted with prominent public function, domestically or in foreign countries and the Heads of International Organizations. Given the PEP’s access to government funds and power to influence government decisions, they are more susceptible to criminal activities such as corruption and, in turn, money laundering to hide these illegal funds. The close family members and business associates would also be considered as PEP for risk classification of the customer under AML compliance.
- Individuals or entities hailing from or are closely connected with high-risk countries
- These high-risk countries are vulnerable to high risk of money laundering due to factors like a high rate of corruption, less transparency around business activities and beneficial ownership, and weaker AML/CFT measures known to have been assisting the countries or organizations supporting terrorist activities.
- The individuals or entities whose behaviour or transactions suggest the presence of ML/FT suspicion
- The customer’s behaviour while establishing a business relationship or conducting the customer due diligence suggests any connection with proceeds or crime or the transactions executed by the customer are contrary to the customer’s profile.
The customers engaged in business are considered as high-risk, or where the customer’s business activities are associated with ML/FT typologies, such as Virtual Assets Service Provider, where large amounts of fiat currency can be easily converted into cryptocurrencies and transferred across the border without actually disclosing the identity or drawing the attention of the authorities.
The AML laws of UAE require the Financial Institutions, VASPs and DNFBPs to apply Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) measures to these customers to manage the higher risk and determine whether they are not connected with any illegal activities, money laundering or financing of terrorism.
Importance of identifying high-risk customers
Identifying high-risk customers and applying required due diligence measures to mitigate the increased risk are critical aspects of an effective AML program. It helps the regulated organization maintain integrity among the stakeholders and customers, safeguard the business from being involved in money laundering or terrorism funding activities, and stay 100% AML compliant.
Protecting your business from financial crimes
Not just directly indulging in money laundering or terrorism financing activities is a federal crime, but indirectly assisting anybody, knowingly or unknowingly, is also a crime punishable under UAE AML regulations. The regulated organizations, whether Financial Institutions, DNFBPs or VASPs, would be subject to heavy monetary fines and sanctions from the Supervisory Authority for executing any financial crime through its business.
Hence, regulated organizations need to identify high-risk customers and apply additional verification measures to prevent the misuse of the business by financial criminals and money launderers.
The regulated organization must use rigorous identity verification checks to detect the customers connected with high-risk parameters like high-risk countries and robust transaction monitoring systems to identify unusual patterns or suspicious customer behaviour.
Once identified, high-risk customers should be subject to EDD measures, which include obtaining additional information and documents about customer identity, financial position (source of funds and source of wealth), frequent, ongoing monitoring, etc.
Meeting regulatory requirements and staying compliant
AML regulations in UAE mandate the regulated organization to apply adequate AML measures and stay 100% AML compliant. Non-compliance with AML regulatory requirements by any regulated organization calls for severe actions from the authorities, including imposing hefty administrative fines, imprisonment, restriction on the business activities or even termination of the business license.
As part of the AML Compliance program, the regulated organization must identify high-risk customers, take adequate mitigation measures, and report to the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) to remain AML compliant and avoid non-compliance penalties.
The regulated organizations must adhere to the UAE’s AML Federal Law, implementing Cabinet Decision and supplementary guidelines issued by the relevant Supervisory Authority. These regulations require the Financial Institutions, DNFBPs and the VASPs to implement AML compliance programs to identify and report suspicious activity. One of the critical aspects of the AML compliance framework is identifying high-risk customers.
Maintaining a solid reputation and business integrity
The regulated organizations need to protect their reputation and integrity to survive in the economy and maintain customer trust. The involvement of the regulated organizations in a money laundering scheme or any other financial crime badly damages its reputation amongst its stakeholders and customers in an irreversible manner. Identifying high-risk customers can help detect and prevent such potential indulgence in financial crime.
Instead, implementing a strong AML culture in the organization and demonstrating a commitment towards AML compliance increases the organization’s reputation in the market. These AML measures could include comprehensive AML policies and procedures, adequate customer due diligence process, imparting AML training to employees, etc. The customers and other stakeholders are more inclined towards working with businesses compliant with the regulatory framework.
Identifying high-risk customers is critical for regulated organizations to protect themselves from getting inadvertently involved in financial crimes, stay compliant with regulatory requirements, and avoid any reputational damage. By implementing effective AML compliance programs, regulated organizations can detect suspicious elements posing higher ML/FT risks and prevent money laundering activities from occurring through their businesses.
Customer Risk Assessment and adequate Customer Due Diligence
It is pertinent to design and implement a robust customer risk assessment procedure and apply adequate Customer Due Diligence (CDD) measures to identify high-risk customers, exposing the business to increased ML/FT risks. This part of AML compliance involves identifying the customers and their Ultimate Beneficial Owners (UBOs) and verifying the customer identity and other information to create the customer’s risk profile and identify any suspicion.
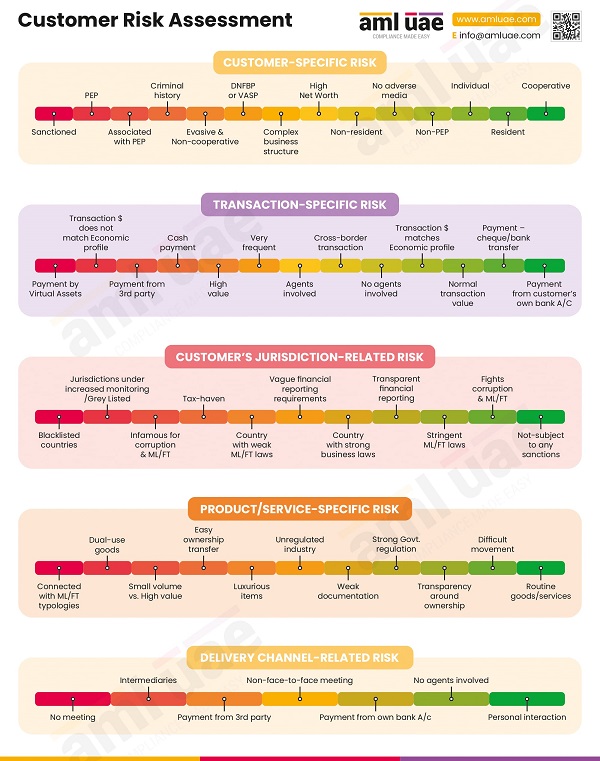
Developing a risk assessment framework
It is essential to assess the risk of each customer the organization is dealing with. The customer risk assessment procedure is about obtaining customers’ identification information, like name, nationality, business activities, etc., to determine the ML/FT risk they bring. The factors to be considered while determining the customer risk are the nature of the customer, its business activities, the geography of the customers, the nature and purpose of the business relationship, transactional parameters – value, mode of payment, etc.
By developing a comprehensive customer risk assessment framework, regulated organizations can adopt a risk-based approach and prioritize the customer due diligence measures depending on the risk associated with the customers. The regulated organisation can design and implement adequate risk mitigation measures by evaluating the specific ML/FT risks associated with the customers.
Performing appropriate Customer Due Diligence
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) measure involves:
- Identifying the customer and verifying the customer’s identity using reliable, independent sources, including the customer’s valid identification documents
- Conducting screening against the sanctions and adverse media to check customer’s background and reputation
- Performing customer risk assessment, based on the customer’s profile and the transactional parameters, to identify the ML/FT risk the customer is posing to the business.
The regulated organizations must design a strong CDD program, including policies, procedures, and controls. The organizations may also deploy AML software to perform CDD, such as using Artificial Intelligence or Machine Learning to screen the customers or create customer risk profiles, evaluating the customer’s identification data and documents.
The AML software can help regulated organizations to identify suspicious activities timely and immediately report the same to the authorities, reducing false positive matches.
The Customer Due Diligence process is incomplete without ongoing monitoring of the customer’s profile to identify changes in customer identification information, and ongoing transaction monitoring to determine whether the customer’s behaviour is in sync with the originally assessed risk or customer rile level needs to be re-evaluated.
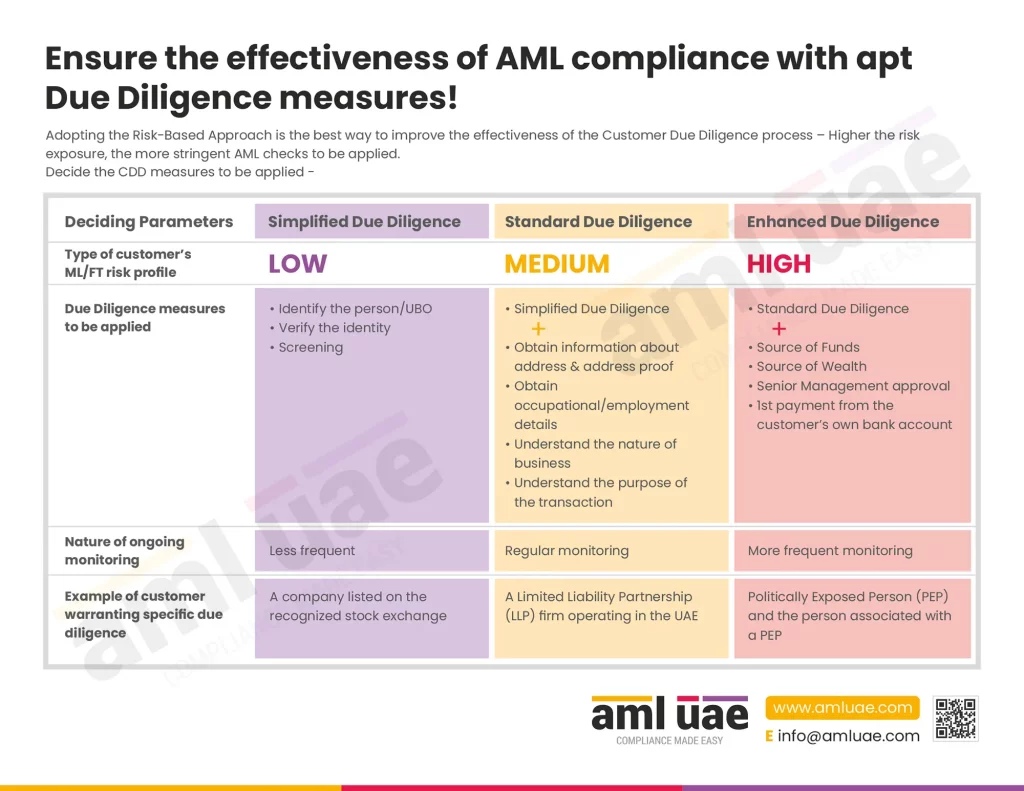
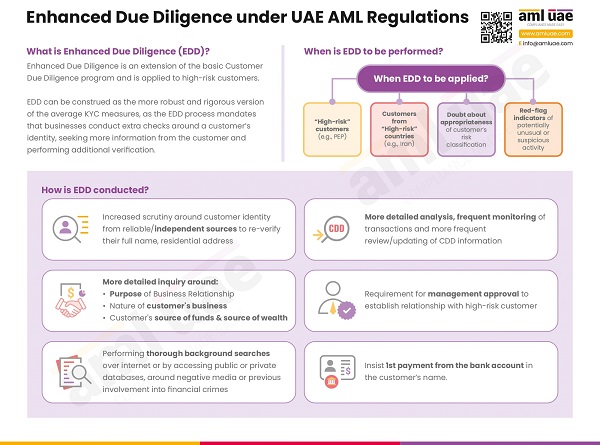
Enhanced Due Diligence for high-risk customers
Application of Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is mandatory for customers identified as high-risk. The EDD is an extension of the CDD process, requiring the regulated organizations to apply additional checks and verification measures to evaluate the customer’s identity (including the beneficial owners and the controlling parties), their financial position, the purpose of the transaction, etc.
EDD involves obtaining information about the customer’s and Ultimate Beneficial Owners’ source of funds and wealth and determining its legitimacy. Further, UAE AML regulations mandate the regulated organizations to ensure that the first payment towards their product or services is received from the customer’s bank account in a bank subject to similar CDD measures. Customers and transactions with high-risk customers are to be subjected to increased ongoing monitoring to assess and detect any unusual patterns or suspicious activities.
No business relationship can be established or a transaction be executed with a high-risk customer without the approval of the regulated organization’s senior management.
For example, suppose a customer is associated with a high-risk country. In that case, the regulated organization must apply rigorous verification measures and implement EDD to manage the increased ML/FT risk associated with a customer hailing from a high-risk country.
Red Flags and potential risk indicators of high-risk customers
Detecting the ML/FT red flags and risk indicators is essential to determining the risk associated with a customer and classifying them as high-risk customers. Here are a few examples of ML/FT red flags that can suggest the involvement of proceeds of crime, money laundering or terrorism financing activities:
Unusual transaction patterns
Transactions inconsistent with a customer’s profile or nature of business activities, unusually large, or series of transactions over a short period can indicate money laundering activities. Additionally, transactions involving unnecessary intermediaries or multiple jurisdictions can raise red flags.
For example, if a customer with a fixed monthly income starts making large value transactions frequently, contrary to its annual income, it indicates suspicion around the source of funds.
Incomplete, fake or inconsistent information
Customers who provide incomplete, incorrect or inconsistent information are red flags, suggesting the customer attempts to hide their identity or disguise the purpose of the transaction. The regulated organizations should be cautious while verifying the customer’s identity and establishing its risk profile to determine the legitimacy of the identification information and validity of the identity documents.
E.g., if a customer provides a different address every time they interact or multiple customers use the same contact number/email ID, suggest a potential money laundering activity involving multiple parties across different jurisdictions. Similarly, if the customer’s identification documents prove to be forged upon verification, a red flag indicates potential involvement in financial crime activities and hence the need to mislead the identification.
High-risk occupations or connect with high-risk business segments
Customers with high-risk business activities, such as gambling, real estate, and precious metals, prone to higher exploitation by money launderers, require enhanced verification measures.
E.g., if a customer engaged in a real estate brokerage business insists on cash payment, it could be considered a potential risk indicator suggesting money laundering activities.
Geographical risk factors
Customers located in or closely connected with high-risk countries, such as those with no or weaker AML regulations, terrorist activity, or high-rate of corruption, should also be considered as high-risk to apply AML/CFT measures.
E.g., a customer from a country mentioned in the FATF’s grey list of countries subject to increased monitoring is to be considered for enhanced customer due diligence measures.
Identifying the potential risk indicators helps the regulated organization proactively detect high-risk customers and apply adequate measures to manage the increased ML/FT risk, stay compliant, and avoid non-compliance penalties.

With AML UAE’s expertise, manage your increased ML/FT risk posed by high-risk customers
Identifying high-risk customers and deploying mitigative measures is crucial for regulated organizations to manage regulatory compliance, safeguard the business from ML/FT vulnerabilities and avoid reputational damage.
AML UAE is an AML Consultancy service provider that offers end-to-end support in your AML compliance journey. We help clients conduct the overall Enterprise-Wide Risk assessment and design the tailor-made AML compliance framework, including controls and procedures to identify high-risk customers and enlist the potential risk indicator and red flags relevant to the business activities. We assist clients in effectively implementing the AML framework by imparting comprehensive AML training to the client’s AML/CFT Compliance Officer and the compliance team.
Stay safe, Stay compliant!
Make significant progress in your fight against financial crimes,
With the best consulting support from AML UAE.
Our recent blogs
side bar form
Share via :
About the Author
Pathik Shah
FCA, CAMS, CISA, CS, DISA (ICAI), FAFP (ICAI)
Pathik is a Chartered Accountant with more than 25 years of experience in compliance management, Anti-Money Laundering, tax consultancy, risk management, accounting, system audits, IT consultancy, and digital marketing.
He has extensive knowledge of local and international Anti-Money Laundering rules and regulations. He helps companies with end-to-end AML compliance services, from understanding the AML business-specific risk to implementing the robust AML Compliance framework.
