Enhanced Due Diligence by Dealers in Precious Metals and Stones: EDD for High-Risk Customers
Precious metals like gold, silver, platinum, and precious stones such as diamonds, sapphires, pearls, etc., are highly vulnerable to money laundering and terrorism financing. The Dealers in Precious Metals and Stones (DPMS) must implement Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) measures to manage the increased financial crime risks arising from high-risk countries or transactions.
Owing to the following inherent characteristics of the precious metals and stones, the products are closely associated with ML/FT typologies and bring the DPMS under the ambit of UAE AML regulations:
- Small size, high value
- Easy to transport
- Used as a store of value
- Can be used as a medium of exchange
- Is acceptable in most parts of the world
- Retains value and is subject to lesser value fluctuation
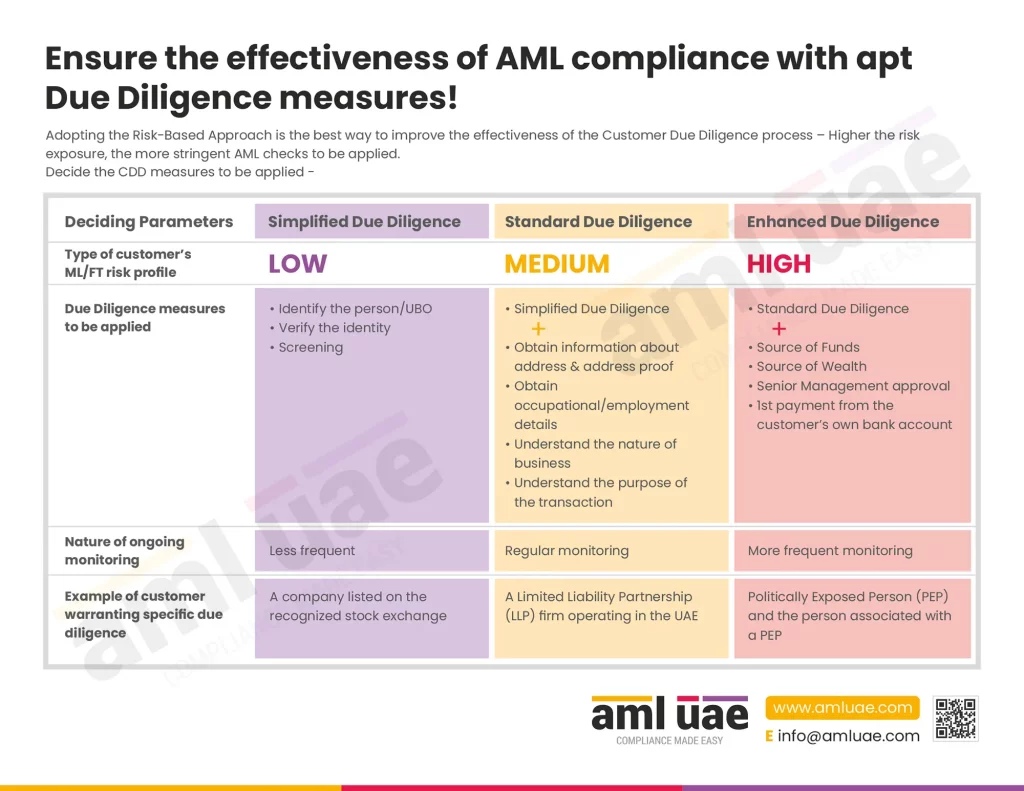
The UAE AML regulations mandate that Dealers in precious Metals and Stones adopt adequate Customer Due Diligence (CDD) measures to manage the ML/FT risks. The DPMS is required to implement enhanced customer due diligence measures when the customer is identified as high-risk.
In this article, we will navigate Enhanced Due Diligence under UAE AML regulations and how dealers in precious metals and stones can implement the EDD measures.
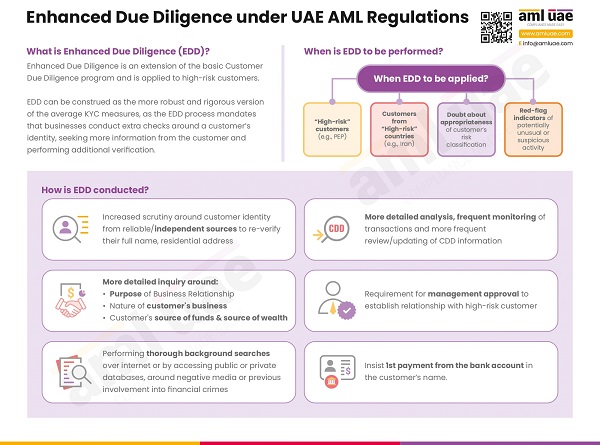
Understanding the concept of Enhanced Due Diligence as per UAE’s AML regulatory landscape?
Enhanced Due Diligence is essential to the overall AML Compliance Program in a Dealer in Precious Metals and Stones. EDD is a subsection of the Customer Due Diligence process, mandatory to be adhered to when dealing with high-risk customers.
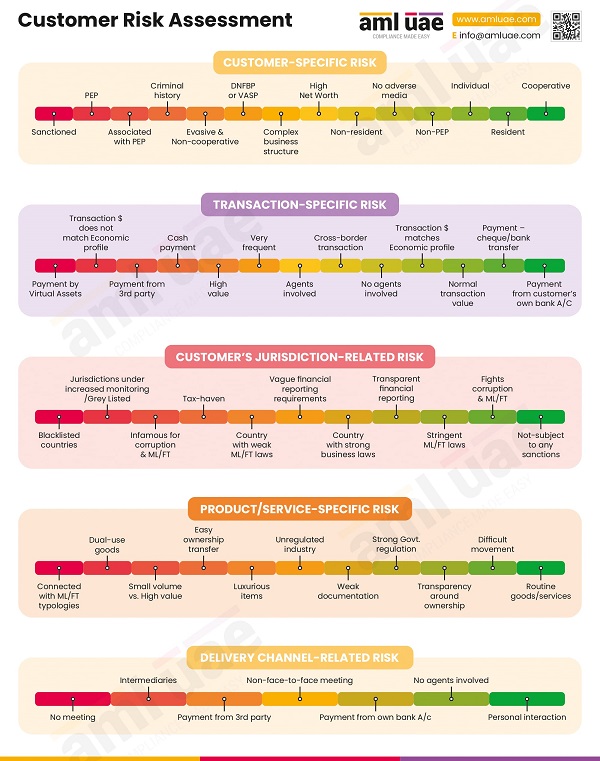
Customer Due Diligence is implemented to identify the customer and its beneficial owners and verify their identity to ensure that the company, knowingly or unknowingly, does not expose itself to financial crime. In this CDD process, the customer’s risk is also assessed, and appropriate risk categorization is done (either as High, Medium, or Low) by performing Customer Risk Assessment. During such a process, if the customer’s risk is assessed to be high, the dealers in precious metals and stones need to deploy some additional checks and verification measures to mitigate the increased risk. This process of applying additional measures to the customer or business relationship is called “Enhanced Due Diligence.”
What are the circumstances when EDD measures are to be applied?
EDD is adopted when the business relationship, customer, or transaction is identified as posing higher money laundering or terrorism financing risks to the business. Such situations may include:
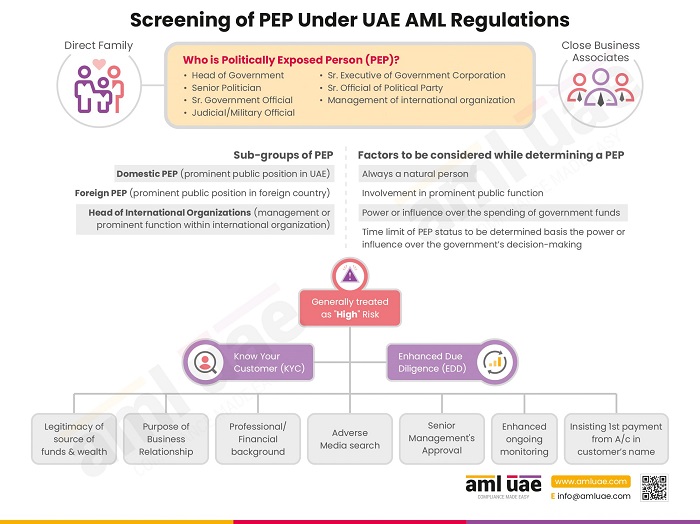
- Business relationship with a Politically Exposed Person (PEP)
- When the customer is associated with a high-risk country
- When the customer is coming from a jurisdiction having a weak or minimal AML/CFT regulatory framework
- Transaction with a customer closely connected with a country notorious for money laundering or terrorist financing activities
- When there is doubt about the accuracy or legitimacy of the information about the customer obtained earlier
- When any ML/FT risk indicator or red flag is observed
What measures must the Dealers in Precious Metals and Stone adopt as part of the Enhanced Due Diligence?
Enhanced Due Diligence is not just restricted to the basic identification of the customers and the beneficial ownership but goes one step ahead of the standard CDD process. Under EDD, the DPMS is expected to implement the following additional measures to manage the higher ML/FT risks:
Additional information and verification measures
Rigorous identity verification measures should be adopted, such as getting certified copies of the documents and verifying them against independent databases.
The dealers and precious metals and stones must make additional efforts to collect more information about the customer, such as looking out for adverse media or negative news about the person. An additional inquiry must be made around the customer’s intended purpose of the business relationship and the nature of the transaction.
Inquiry about the Customer’s Source of Funds and Wealth
Since precious metals and stones are high-value items, the DPMS must inquire about the customer’s source of funds for the proposed transaction. Further, to determine the customer’s financial position, the DPMS must seek information about the customer’s source of wealth to determine whether the value of transactions and the customer’s finances are aligned.
Obtaining the information is not sufficient. The dealer in precious metals and stones should also determine the legitimacy of the declared source of funds and wealth using reliable sources such as the customer’s bank statement, audited financial statement or Balance Sheet, Tax Return, Pay slips or employment contract, etc.
Obtaining senior management approval
Given the increased financial crime risk involved in the business relationship, the UAE AML regulations mandate the DPMS to seek approval from the senior management before establishing such a relationship. Further, management approval must also be obtained when executing a transaction with high-risk customers.
1st payment through customer’s own bank account
When engaging with high-risk customers, the DPMS must have the first payment processed through the customer’s bank account with a bank having similar Customer Due Diligence measures.
This implies that the dealers in precious metals and stones must not execute the first transaction in cash with high-risk customers.
Increased ongoing monitoring
Once high-risk customers are onboarded, it is the regulatory obligation of the DPMS to monitor the customer profile and the transactions pertaining to high-risk business relationships. Such customers must be subject to an increased frequency of CDD information updates (for example, once in six months). Further, the transaction must be closely monitored to ensure that the same is in accordance with the customer’s risk profile and financial information furnished earlier and consistent with the customer’s nature of business activities.
This will help the DPMS identify any suspicious activities or unusual transactions indicating the involvement of financial crime risks.
Undertaking these additional checks and measures during Enhanced Due Diligence will help the DPMS better understand the customers and effectively manage the risk, especially increased ML/FT risks.

What are the critical elements for implementing Enhanced Due Diligence in the DPMS sector?
For the quality implementation of the Enhanced Due Diligence process, the Dealers in Precious Metals and Stones need to adopt the following components, ensuring effective mitigation of the increased risk and AML regulatory compliance:
Customer Risk Assessment
The DPMS must clearly lay down the guidelines for when the customer shall be classified as high-risk, warranting the application of the EDD measures.
For this, the customer risk assessment methodology must be well-defined, allowing the company to detect the high-risk posing business relationships timely.
Well-crafted EDD Program
The company must design and maintain a comprehensive Enhanced Due Diligence Program, providing practical guidelines for the compliance team to manage the higher risk of money laundering or terrorism financing. The EDD policy must prescribe the additional information to be sought from the customer, the documents to be obtained, and the resources to be relied upon for independent verification.
The methods and frequency for performing ongoing monitoring of high-risk customers must be well-documented.
EDD Training to the Team
The circumstances requiring the application of the EDD process and the additional measures to be applied must be communicated with the team. Regular training must be conducted to ensure that the team understands the EDD program and can apply necessary checks on a timely basis.

Potential red flags suggesting higher ML/FT risks when DPMS must apply EDD measures
Given the nature of the products and services involved, the following are some of the risk factors when the Dealers in Precious Metals and Stones must adopt the Enhanced Due Diligence process:
- When the transaction appears to be complex, involving multiple parties across different locations
- Customer is a Politically Exposed Person or a close associate
- When the customer insists on making a payment using cash, even when the transaction value is high
- Inconsistency between the nature of the customer’s activities and the purpose of the transaction (Non-Profit Organization buying 1 kilogram of gold)
- When the customer is hailing from or conducting business in high-risk countries
- Customer making unreasonable request of converting the form of precious metals to ordinary objects
- Customer making series of small value transactions
- Payment being routed through an unrelated third-party account
Let AML UAE assist you in implementing the robust Enhanced Due Diligence mechanism to safeguard your precious metals and stones business
Implementing EDD measures in the DPMS sector is pertinent to manage the risk associated with precious metals and stones. AML UAE can assist you in developing the EDD program for your jewellery business, ensuring that you rightly identify high-risk customers and manage these risks with suitable AML measures and controls. We assess your business exposure to financial crime risks and customize the easy-to-implement AML/CFT Compliance framework, focused on detecting and preventing the exploitation of precious metals and stones for financial crime and staying AML Compliant.
Enhance the quality of your AML Program with a comprehensive Enhanced Due Diligence Process!
Make significant progress in your fight against financial crimes,
With the best consulting support from AML UAE.
Our recent blogs
side bar form
Share via :
About the Author
Pathik Shah
FCA, CAMS, CISA, CS, DISA (ICAI), FAFP (ICAI)
Pathik is a Chartered Accountant with more than 25 years of experience in compliance management, Anti-Money Laundering, tax consultancy, risk management, accounting, system audits, IT consultancy, and digital marketing.
He has extensive knowledge of local and international Anti-Money Laundering rules and regulations. He helps companies with end-to-end AML compliance services, from understanding the AML business-specific risk to implementing the robust AML Compliance framework.
