AML Transaction Monitoring: A powerful tool to detect financial crimes
Ever received a call from your bank to confirm if you have conducted a specific high-value transaction? If yes, then that is what transaction monitoring means. They know your routine transactions. If they see one unusual transaction and different from your general banking behaviour, they make a confirmation call.
Financial criminals conduct fraudulent activities by harnessing loopholes in regulations. They create an air of legitimacy around their scheme, company, and transactions.
Transaction monitoring can help detect patterns of suspicious behaviour and financial crimes to and from customers. That is why it is a significant step in companies’ and governments’ AML and CFT programs. With transaction monitoring, you can detect crimes before their occurrence or in their early stages. Timely detection saves you from the repercussions.
This article aims to explain the concept of transaction monitoring, its significance, and the best monitoring practices.
What is AML transaction monitoring?
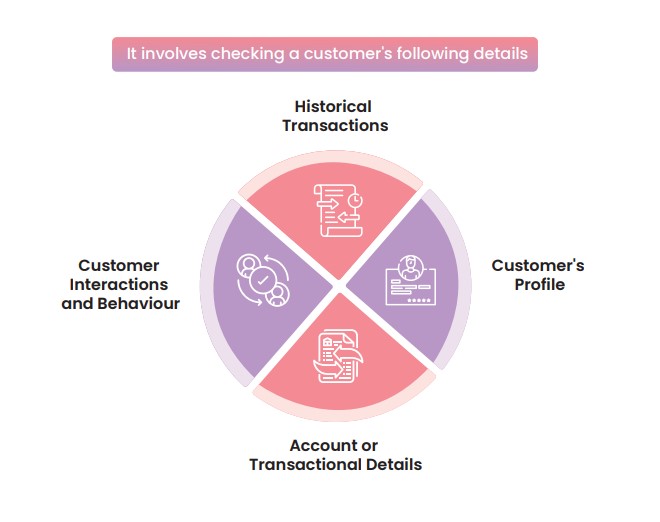
Transaction monitoring means regularly keeping a close watch on the transactions. It involves checking a customer’s historical transactions, customer’s profile, account details, and interactions. These checks enable the identification of possible customer risks and the prediction of their future behaviour.
You can track the transactions in real-time during their occurrence to block them and prevent fraud. Alternatively, you can check transactions to identify any set patterns after their occurrence. Conduct periodic transaction monitoring to check the customer’s behaviour in terms of irregularities or set patterns.
Thus, financial institutions, as well as DNFBPs, must conduct frequent checks of their transactions.

Significance of AML transaction monitoring
Generally, anti-money laundering regulations in countries include the practice of transaction monitoring. It is mandatory for entities to track suspicious customers, suppliers, or transactions.
Entities have started using transaction monitoring systems to detect suspicious transactions. But it also requires human intelligence and experience to separate fraudulent transactions from non-fraudulent ones.
A constant check on customers’ activities is essential to avoid financial crimes. Transaction monitoring allows entities to adopt a risk-based approach, wherein the monitoring is done based on set rules defined considering the customer’s risk profile developed and the nature of transactions executed by the customer.
Based on the risk profile, you must monitor the customers. For a high-risk client, you need to adopt an advanced level of transaction monitoring.
Nowadays, criminals have advanced ways of conducting financial crimes in the times of the online, digital world. The complexity of money laundering and terrorist financing has increased, which requires a measure that can spot right from wrong. So, transaction monitoring with the definition of a clear rule is crucial to identifying criminal activities.
Furthermore, the transaction monitoring framework gives confidence to regulators and stakeholders of the organization. It shows the seriousness of entities toward detection of financial crime. It leads to a safe business ecosystem in the country and builds trust between existing and new partners.
Steps to an effective transaction monitoring program
Transaction monitoring is a risk-based approach with the following steps:
1. Risk assessment of your business
Identifying risks your business faces from customers, products and services, and operating environment is critical for your AML compliance. For this, you must conduct a detailed analysis of the industry in which you operate.
Analysis of risk parameters will determine your business’s risk appetite. A deep understanding of the risks you take as an entity and the measures you use to cover these risks is crucial. Also, you get to know what types of customers you will be handling, types and volumes of transactions and related risks thereof.
2. Define red flags of suspicious transactions

To ensure the correct identification of suspicious transactions, you must know what it looks like. For this, you must define the red flags your employees will look for while reviewing transactions or the rules set in the transaction monitoring solution. Some of the red flags can be:
- Transactions involving large amounts of money,
- A sudden new transaction unusual for a customer (nowhere like any other transactions done before),
- Several small transactions of the same type involving one or more accounts/persons in a short time,
- Inconsistency of the transaction with the customer’s economic profile,
- The transaction is directed to or from a high-risk country or a jurisdiction featured in the sanction list,
- Customer’s insistence on having no face-to-face communication always.
You must feed these red flags into the transaction monitoring system to generate alerts when witnessed. The team handling this system receives an alert notification. The entity can conduct a further investigation based on the alert to classify it as suspicious.
3. Create transaction monitoring rules
You must create transaction monitoring rules based on your risk appetite and red flag indicators. The system for transaction monitoring will have to be aligned with these rules to identify suspicious transactions. The rules may be created around the following:
- The maximum amount of a transaction,
- Number of unusual transactions from a customer,
- Number of small transactions, after which the system generates an alert,
- Transaction directed to or from a high-risk jurisdiction.
The monitoring system analyses the transaction against the set rules. Based on the defined rules, the system should be able to identify the suspicious pattern or characteristic and generate a trigger or alert for the same.
You must optimize these rules periodically based on historical results. Changes in rules will make the process more accurate, resulting in fewer false positives.
4. Review the generated alerts
You must review these alerts generated for suspicious transactions. The analysts must conduct a manual evaluation to check if the pattern or behaviour is suspicious. To produce a detailed report, they must collect all relevant information for that transaction.
If you find it suspicious, prepare a report of the investigation conducted, which should be shared with the senior management for sign-off. Basis your evaluation, you may even drop the alert, but document the reason.
Best practices of a robust AML transaction monitoring program
Some of the best practices you can adopt for transaction monitoring include:
Remain up-to-date with regulations
Keep an eye on the local and national regulations for combating money laundering and other financial crimes. Compliance with them is essential. With knowledge of all rules and regulations, you can update your red flags, optimize the monitoring rules and identify suspicious transactions efficiently.
Know about your industry and products/services
You must have deep knowledge of your sector and products/services to ensure effective transaction monitoring. Awareness of industry-specific risks, customer demographics, and product/service weaknesses can help create effective monitoring rules.
Furthermore, keep updating your knowledge on these factors. The updated information helps you improvise your transaction monitoring solution and timely capture all money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
Create an exhaustive list of transaction monitoring rules
Consider all the possible red flags for your industry and product/services while creating transaction monitoring rules. These rules must encompass a range of simple and complex scenarios to detect all possible suspected transactions.
Criminals keep updating their crime techniques to take advantage of your operations, processes, products, customers, etc. Similarly, you must frequently update these rules to stay on top of your criminal typologies.
Ensuring quality of AML transaction monitoring
Entities must try to avoid making transaction monitoring an operational, time-bound task. You must consider it as an action against decreasing or eliminating financial crimes. Accordingly, entities must base the employees’ performance on the quality and efficiency of transaction evaluation, not the volume of transactions handled.
Document the AML monitoring scenarios
The transaction monitoring system generates alerts if a transaction is against any rules fed into the system. Then, the analyst evaluates it comprehensively by collecting all related and relevant information.
You must document all this information, analysis, and insights. Documentation helps develop a precise, comprehensive scenario. And documentation of all these scenarios helps create more rules and logic to better your transaction monitoring process.
Do not assume that one size fits all
Do not oversimplify the risk scenarios. Create detailed, to-the-point, granular-level characteristics to identify risky behaviours or patterns of customers or transactions. The clarity in scenarios enables better comparison with the rules to identify suspicious transactions and reduce the possibility of false positives.
Do not have too many risk scenarios
Entities create an exhaustive list of risk scenarios to capture every possible suspicious transaction. But in this process, they forget to remove duplicates and non-contextual scenarios. With such an extensive list of possible risk scenarios, employees’ workload increases, and the quality of alerts decreases. So, while creating scenarios, avoid overlap and add relevant context to each.
Use artificial intelligence in transaction monitoring
Only rules based on logic will not be sufficient for effective transaction monitoring. You must have AI-based transaction monitoring systems to generate more insights and identify red flags that human eyes can overlook. Artificial intelligence can catch any pattern or behaviour that slips through the manual monitoring rules.
AML UAE’s role in transaction monitoring for entities
Since you understand the importance of transaction monitoring in your AML efforts, make it a part of your AML compliance program. Imbibe the best transaction monitoring practices to be 100% compliant with AML regulations and safeguard your business interest against financial crimes.
AML UAE is a leading provider of AML/CFT consulting services. We help our clients develop an effective AML compliance framework for their operations. Transaction monitoring and suspicious transaction reporting are essential parts of such frameworks.
We help clients with ML/FT risk assessment, determination of red flags, and creation of transaction monitoring rules aligned with your business profile. We can also assist you with selecting effective transaction monitoring software and implementing it with our AML experts’ support.
With AML UAE, you can monitor your transactions with relevant rules, making detecting suspicious transactions easier and smoother. Your chances of true positives increase, and the investigation quality improves.
Strengthen your transaction monitoring capabilities with AML UAE’s expert AML/CFT consulting services.
Contact AML UAE to get started.
Our recent blogs
side bar form
Share via :
About the Author
Dipali Vora
Associate Company Secretary
Dipali is an Associate member of ICSI and has a Bachelor’s in Commerce and a General Law degree. She has an overall experience of 7 years in the compliance domain, including Anti-Money Laundering, due diligence, secretarial audit, and managing scrutinizer functions. She currently assists clients by advising and helping them navigate through all the legal and regulatory challenges of Anti-Money Laundering Law. She helps companies to develop, implement, and maintain effective AML/CFT and sanctions programs. She knows Anti-money laundering rules and regulations prevailing in GCC countries and specializes in Enterprise-wide risk assessment, Customer Due-diligence, and Risk assessment.
FAQs on Transaction Monitoring
When an entity identifies a suspicious transaction of financial crime, the Compliance
Officer or the MLRO (Money Laundering Reporting Officer) must file the STR to the
Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU), without any delay.
Suspicious transactions are the ones that constitute the proceeds of financial crime,
are intended to be used in financial fraud activities, or are related to the crimes of
money laundering, terrorism financing, corruption, bribery, drug trafficking, and any
other illicit activities.
In a transaction, from AML perspective, the red flags could be around the change in
the customer’s identification, doubt around the sources of funds involved, transaction
associated with high-risk countries, inconsistencies in the transactional pattern, etc.
Yes, there can be more than one AML red flag indicator in a transaction.
Transaction monitoring is essential to identify suspicious transactions, so that ML/FT
activities can be timely reported. Further, transaction monitoring is also essential to
complete the AML/CFT efforts of the entity.
KYC is related to identification of the customer and verifying the identity. While
transaction monitoring is continuously reviewing the customer’s transaction
executed in course of business relationship.
Transaction monitoring rules are the thresholds and the logic configured by the
entity in its AML program – tools and systems – aimed to analyze the transactions
and generate an alert when the activities match the risk criteria defined in these rules.
Generally, the key challenges around transaction monitoring program are data
integrity, integration of the monitoring system with business’s legacy system,
generation of large number of false positive alerts, not updating the monitoring rules
and systems periodically, etc.


