Customer Due Diligence in UAE is a regulatory requirement
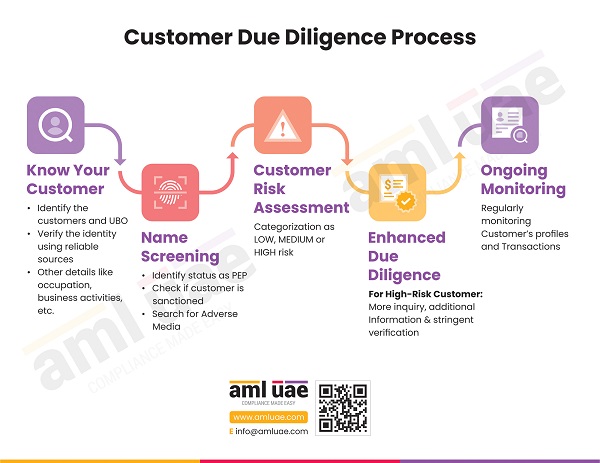
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is all about identifying potential customers and checking their authenticity and legitimacy. In addition, it means cross-verification of the details provided by the customer for their legal validity and accuracy. The CDD meaning remains the same, but the procedures change across the industries. In total, there are four aspects of CDD, namely, simplified, standard, enhanced, and ongoing.
Different aspects of customer due diligence program
1. Simplified due diligence
The process of simplified customer due diligence comes into the picture when the customer belongs to a low-risk category. The Designated Non-Financial Business and Professions (‘DNFBP’) is required to know the customer’s identity and basic details under a simplified customer due diligence process, and there is no need for carrying out detailed due diligence.

2. Standard due diligence
Generally, DNFBPs adopt Standard Customer Due Diligence procedures for the majority of the customers. As a part of this process, the identity of the respective customer is verified from several reliable sources. In addition to that, DNFBPs also determine and evaluate the nature of the customer’s business or the customer’s purpose for entering into a transaction with the DNFBP.
3. Enhanced due diligence
Enhanced Due Diligence is usually required for only those customers who have a high-risk quotient and are more likely to get involved with money laundering or financing of terrorism. There are undoubtedly quite a few factors that clearly establish that a particular customer hails from a high-risk background. For instance, politically exposed people (PEPs) are usually categorized as high-risk customers and require enhanced customer due diligence.
With the help of enhanced customer due diligence, the information of the customers is verified, and critical information like the origin or the source of their funds, source of wealth, and the primary purpose of the transaction is obtained.
Further, as a part of the enhanced CDD measures, it is ensured that the customer makes the payment from the bank account in his own name.

It is also required to obtain approval from the senior management before entering into a transaction with high-risk customers. Once you meet the above Enhanced Due Diligence Requirements, you can carry out transactions with the customer.

4. Ongoing due diligence
The financial situation of a customer changes over time, and it becomes inevitable for the DNFBPs to take this into consideration for better execution of the business plans in accordance with the AML/CFT regulations. In order to keep up with the constant change in the financial transactions, DNFBPs should observe the actual movements of the respective customers. Therefore, the risk profile or categorization of the customer should be monitored on a regular basis or specifically upon identification of certain indications arising from doubt about the status of the customer.
Fundamentals of customer due diligence
1. Identification of customer
2. Beneficial ownership
3. Business Relationship
What risks does a reporting entity face if it fails to carry out Customer Due Diligence (CDD)?
If a reporting entity like a financial institution, DNFBP, or VASP does not carry out Customer Due Diligence, it harms its reputation and exposes itself to various risks like money laundering, terrorist financing, proliferation financing, and corruption. It may also be subjected to administrative penalties.
When is customer due diligence required?
The need to apply the AML CDD process comes into the picture when a business organisation is required to abide by AML/CFT regulations and intends to establish a business relationship with a potential customer.
In line with the Customer Due Diligence Policy and Procedures, businesses try to understand the following and take adequate CDD measures:
- Why is an account being opened?
- How will it be used?
- What will be the nature of transactions?
- What will be the volume and frequency of transactions?
The business must verify the customer’s identity and assess the risk profile. Therefore, DNFBPs/FIs must carry out the Know Your Customer (KYC) procedure as part of CDD compliance procedures in the following situations.
- Customer Due Diligence becomes mandatory and simply inevitable at the time of entering a new business relationship with an individual or a legal entity. This is important in order to verify the identity of the customer. When undertaking the CDD process for a new customer, the customer's risk profile is also assessed, and the applicability of enhanced due diligence is determined
- Various occasional transactions warrant customer due diligence measures. It may involve amounts of money beyond a particular threshold or entities in high-risk foreign countries.
- Business organizations who suspect the involvement of their customers or proposed customers in activities such as money laundering or financing of terrorism should impose KYC, CDD checks.
- When it is observed that the identification documents provided by potential customers are inadequate or unreliable, or suspicious, the implementation of KYC CDD requirements comes into play.
When is CDD conducted?
CDD is conducted:
1. before entering into a business relationship or
2. during the course of entering into a business relationship or
3. before opening an account or
4. during the course of opening an account or
5. before carrying out a transaction with a new customer
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Process Steps:
Step 1 - Collecting data
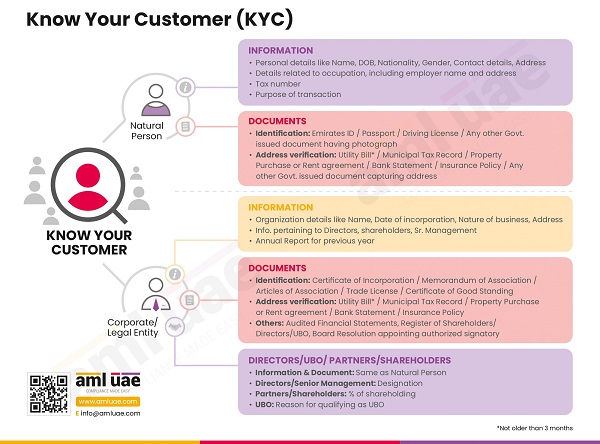
The first step of CDD is to get the essential information from customers or potential customers. A Client Due Diligence Form or KYC form can be maintained for this purpose. The information to be obtained for the purpose of AML due diligence includes the following:
Customer Due Diligence for Natural Persons
- Complete Name
- Address of the customer
- Contact numbers
- Additional/ alternative contact numbers
- Legit, accessible, and working email address
- Place of birth
- Date of birth
- Nationality
- Gender
- Government issued identification number
- Occupation
- Signature
Customer Due Diligence for Legal Entities
- Name of the business entity
- Type of the business entity
- Nature of business the entity is into
- Date and place of establishment
- Information related to the board of directors
- Certificate of establishment/incorporation
- Information related to shareholders or ultimate beneficial owners
- Annual report for the previous year
- Information pertaining to senior management
In addition to that, as a part of the AML customer due diligence, the wealth profile of customers, irrespective of whether the customer is an individual or business entity, is to be checked as well. The wealth profile includes detailed information related to the source of income, approximate networth, and average annual revenue.
Step 2 - Verification
The second step of the CDD program is to verify all the information that has been collected at step one. Again, it is essential to note that most of the collected data can be confirmed with the help of a government agency's site or any reputable independent institution. For instance, documents like identity cards, tax receipts, and passports cannot be verified on the respective Government Portals on the basis of the unique number associated with them.
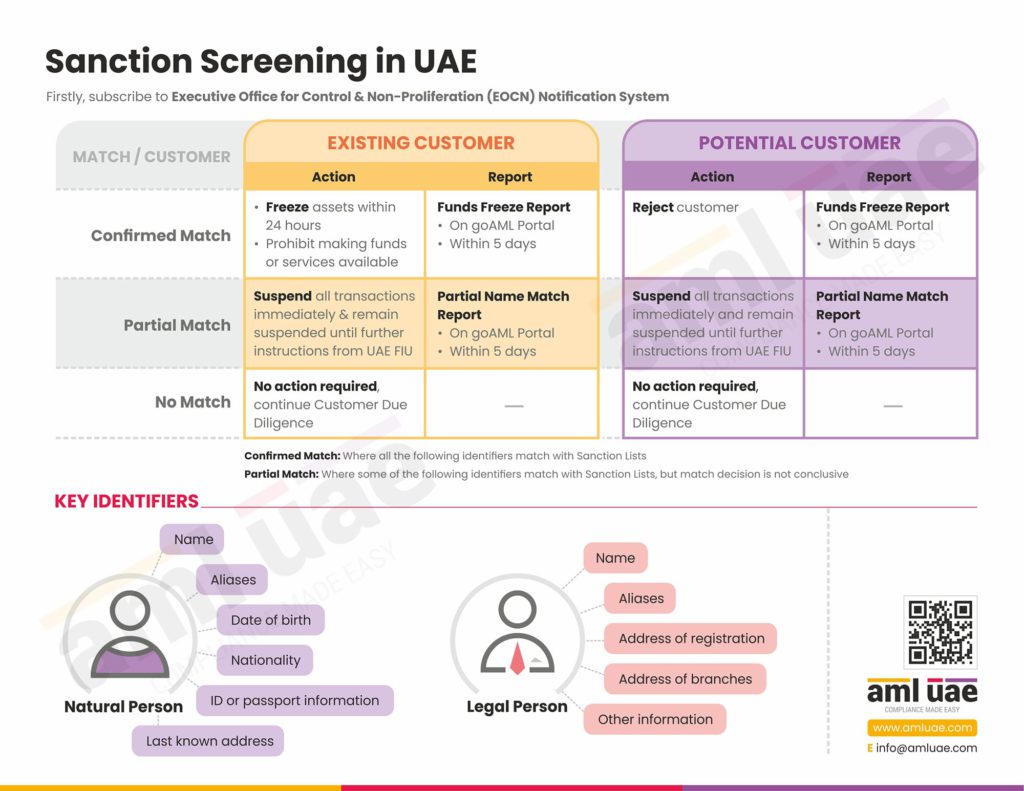
Step 3 - Name screening
Name screening is done in order to see if any customer belongs to a high-risk profile or not. At this point, businesses try to find out whether the customer is on the national or international Sanction List or not. The primary objective behind carrying out the process of name screening is to check that the customers do not fall under the following categories:
- Criminals
- Terrorists
- Politically Exposed Person (PEPs)
- Reported in Media with alleged involvement in any criminal activities
- Sanctioned individual or an identity
Step 4 - Risk profiling
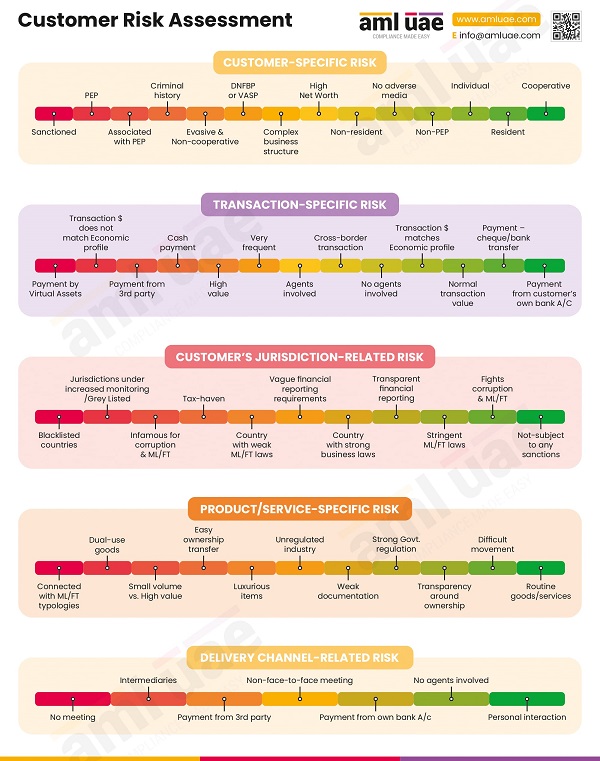
At this stage, the AML Compliance Officer determines the risk level of each customer or potential customer based on various factors. While performing risk-based customer due diligence, the following risk factors are taken into consideration:
- Type and nature of business relationship/transaction
- Nationality of the customer
- Political exposure of the customer
- Mode of payment (Cash, Bank Transfer, Cheque)
- Networth of the individual
- Documentary evidence available
- Amount of transaction
- The complexity of business structure
- Local/international business
- Transaction with a customer based in a blacklisted country
- Transaction with a customer based in a graylisted country etc.
Customer Risk Rating
Once the risk profile is assigned to a customer, DNFBPs and FIs can decide the type of monitoring and level of controls to be imposed while dealing with such customers.
Step 5 - Ongoing monitoring
Once the Customer Due Diligence process is completed and necessary decisions around risk classification have been made, regular monitoring of the customer's risk profile cannot be overlooked. Monitoring should be carried out regularly for identified accounts for all financial transactions. The customer's behaviour, along with accounts and transactions, must be compatible with the usual activities, and this needs to be tracked or overviewed at all costs. Depending upon the risks associated, ongoing due diligence frequency is determined.
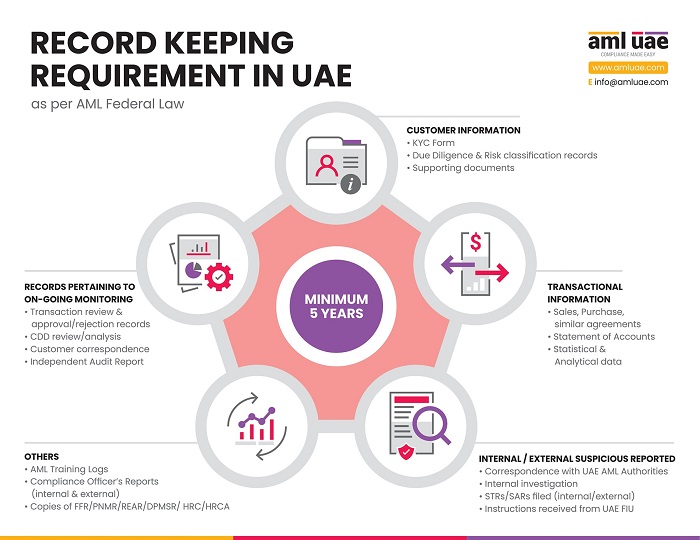
Step 6 - Record keeping
This is the final stage of the entire AML CDD process. At this stage, one has to maintain the CDD related records in accordance with the retention policies of the business organization and as prescribed under AML/CFT regulation. In the UAE, AML/CFT regulations require maintenance of Client Due Diligence and other AML/CFT-related records for the period of 5 years from the relevant dates.
A systematic record-keeping facilitates the DNFBPs to meet its reporting obligation under AML/CFT regulations and furnish such details to the relevant supervisory authorities as and when demanded in the context of any Suspicious Transaction Report filed by the DNFBP.
Why Customer Due Diligence is important
- Customer due diligence ensures that the regulated entity applies CDD procedures risk-sensitively.
- The CDD process provides a comprehensive view of the risk associated with a business relationship.
- The Customer Due Diligence Policy ensures that the regulated entity identifies beneficial owners and the rationale behind customers using a complex corporate structure.
- The CDD procedures also add an element of flexibility where the customers can not provide common forms of identification and alternative ways of verifying their identity without impacting the business.
AML Customer Due Diligence Checklist
Here is the CDD checklist that the compliance team must follow to ensure that they don’t miss out on any of the customer due diligence steps:
Here is the CDD checklist that the compliance team must follow to ensure that they don’t miss out on any of the customer due diligence steps:
- Collect Customer ID and Residential Proof
- Verify Customer ID and Residential Proof
- Perform screening against the UAE Local Terrorist List and UNSC Sanctions List
- Perform Customer Risk Assessment
- Ongoing Monitoring of Business Relationships with Customer
- Record Keeping for 5 Years
Enhanced Customer Due Diligence Checklist
- Obtain additional ID verification documents to the extent necessary
- Understand and document the nature of business and the purpose of transaction
- Obtain and verify the source of funds
- Obtain and verify the source of wealth
- Insist on first payment coming from the customer’s own bank account
- Understand the reasons behind complex legal structure if applicable
- Perform background checks (Internet searches, Sanctions check, Criminal history check, etc.)
- Obtain top management approval for customer onboarding
- Customers to be placed under frequent monitoring for ongoing due diligence of customer information and transactions
Ongoing Customer Due Diligence
Ongoing customer due diligence is a recurring requirement considering the risks associated with a customer. If the customer happens to be a High-risk customer, he should be placed under more frequent monitoring and CDD refresh.
Circumstances requiring KYC refresh:
- Changes in the beneficial owner
- Customers making unusual transactions not aligned with their profile
- Changes in business relationship with a customer
- Changes in ownership structure at the customer’s end
Final words
Anti Money Laundering Customer Due Diligence, whether simplified, standard, enhanced, or ongoing, is an important element of an effective AML CFT Program. Customer Due Diligence is the primary responsibility of the compliance team and frontline employees. Customer Due Diligence checks help identify red flags early and save an organisation from entering into a wrongful transaction and business relationship. Use the above KYC Due Diligence checklist and counter ML/TF risks.
AML UAE provides consulting services on customer onboarding and KYC process, CDD, and risk profiling of customers. If you are looking to automate your CDD functions, we can help you with the customer due diligence software. We also provide training on customer due diligence procedures and help you comply with UAE AML laws and regulations.
Our recent blogs
side bar form
Share via :
FAQs - Customer Due Diligence
Customer due diligence is important to avoid dealing with customers that can be a threat to your business in terms of money laundering or terrorism financing. CDD process helps verify the identity of customers, analyse their risk profile, and check their presence in Sanction lists to comply with AML/CFT regulations.
Effective screening requires accurate data preparations, comprehensive investigation, and sophisticated matching. Here are the critical requirements for effective screening:
- Identification of applicable sanctions lists
- Collating and auditing the source data ahead of the screening
- Define roles, responsibilities, and procedures for sanctions screening
- Precise screening against a wide variety of risk sources
- Screening of international data
- Systematically screening around the complete business enterprise
- Integrating data collected from multiple sources
- Customizing match rules and workflows
- Eliminating the scope of false positives
- Demonstrating enhanced customer due diligence
- Eliminating unnecessary repetition of review work
To improve customer due diligence, apply a risk-based approach to enable corrective actions as per the risk profile of customers. Look out for red flags during the journey of forming a business relationship with your clients and keep documenting to avoid missing out on any unusual activity.
- It makes sure that the customer or potential customer is the one he claims to be
- It protects the ecosystem and business environment from any sort of fraudulent activities like impersonation or identity fraud
- It makes sure that the organization remains compliant with the established laws and regulations of the regions or markets of operations
- Businesses can assist law enforcement in a hassle-free and straightforward manner
The 4 customer due diligence requirements are:
- Customer identification and verification
- Ascertaining the nature and purpose of the business relationship
- Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) identification and verification. PEP identification and verification.
- Ongoing transaction monitoring
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is a compliance process of identifying customers and ensuring they are who they claim to be.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) in Know Your Customer (KYC) process is the foundation based on which businesses collect and verify information pertaining to a customer and determine the money laundering risks associated with them.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is a control mechanism employed by a business to adhere to the risk-based approach adopted by it in relation to money laundering risks. It helps identify the money laundering risks associated with a customer and decide whether to onboard, reject or report a customer to the AML regulatory bodies of the country.
Businesses follow a risk-based approach while identifying and mitigating their money laundering risks. Depending upon the nature and size of the business and the risk profile of a customer, ongoing customer due diligence is undertaken by a business. helps them identify, manage, and mitigate their money laundering and terrorist financing risks.
Here are the characteristics of an effective transaction monitoring program:
- An effective transaction monitoring program is based on the Business Risk Assessment (BRA) performed by the business, taking into account its money laundering, terrorist financing, and proliferation financing risks
- An ongoing monitoring program is regularly audited and maintained to ensure that it effectively operates and helps keep risks within the risk appetite of a business, and applies to all transactions and services provided by a business
- It helps identify and mitigate ML/TF issues
- It establishes accountability to ensure that the money laundering and terrorist financing typologies are reviewed in a timely manner
- An effective transaction monitoring program is regularly managed to ensure that red flags are appropriately addressed and risk-adjusted
- It ensures that the business relationship is always monitored
As per UAE AML Laws, FIs, DNFBPs, and VASPs are supposed to identify and verify a customer before entering into a business relationship with them.
DNFBPs, FIs, and VASPs are required to carry out the Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Process. The reporting entities appoint Money Laundering Reporting Officer or AML Compliance Officer to oversee the overall AML compliance function. The MLRO/AML Compliance Officer ensures that the CDD process is clearly laid out and operating as intended.
As per UAE AML Laws, reporting entities are required to maintain Customer Due Diligence Records for a minimum period of 5 years.
Banks and Financial Institutions carry out KYC or Customer Due Diligence (CDD) process before onboarding a customer and during the course of a business relationship. It’s vital for banks to know the kind of money laundering and terrorist financing risks carried by a customer. Banks collect identification documents and verify them to ensure that the customer is the one who they claim to be. Further, it continuously monitors the business relationship with the customer and analyses key changes to ML risks over time, and applies necessary controls to mitigate those risks.
- CDD is necessary to identify ML/TF risks associated with a customer
- Customer Due Diligence is necessary to comply with the AML Laws of UAE
- CDD is necessary to establish a business relationship with a customer
- CDD is necessary to detect suspicious activities and transactions and report them to AML regulatory authorities
- CDD is necessary to apply controls commensurate with the risks associated with a customer
All Financial Institutions, DNFBPs, and VASPs need to have a clearly defined Customer Due Diligence policy and procedures.
Documenting and following a Customer Due Diligence (CDD) policy is a legal requirement. However, it isn’t easy to carry out CDD checks manually. Customer Due Diligence software can help you meet legal requirements, manage risks, and make informed decisions. Automation is the key to successfully implementing CDD policy and procedures.
Adverse media searches or negative news searches help reporting entities carry out a risk assessment of a customer. Sometimes a customer who has cleared all the CDD checks, including identification, verification, PEP, and UBO, is found to be a criminal. A plain Google search can provide valuable information about a customer while determining their risk profile.
The UAE AML Laws provide a broad framework under which FIs, DNFBPs, and VASPs have to operate. Reporting entities are free to define their own policies and procedures to carry out the customer risk assessment. As per globally accepted best practices, various factors like product, service, geographic location, and customer profile are considered to arrive at the risk rating associated with a customer. However, businesses are free to employ their own methodology depending upon the nature and size of their business to carry out the customer risk assessment, and it can differ on a case-to-case basis as long as the methodology considers the risks associated with money laundering, terrorism financing, and proliferation financing. To conclude, there is no prescribed methodology including risk factors and categories, and hence the number and detail of the risk assessment criteria can vary.
There is no specific requirement that reporting entities have to update their customer information at a specific interval. The FIs, DNFBPs, and VASPs have to employ a risk-based approach and carry out reKYC on a regular or periodic basis.
Yes, UAE AML Laws require DNFBPs and VASPs to adopt a risk-based approach while establishing business relationships with their customers. There is no common standard that the reporting entities have to follow while collecting information about the ultimate beneficial owner as a part of the CDD process. As per the globally accepted best practices, anyone owning 25% or more of the equity shares in the company is considered to be a UBO. However, nothing in the law restricts a reporting entity from collecting information about individuals who own less than 25% of the shareholding in the company.
The reporting entities are required to obtain a lot of information while onboarding a customer as part of the CDD program. Based on the KYC documents, screening, and various risks associated with the customer, the customer’s risk profile is developed. This risk assessment needs to be used as a baseline against the customer’s business activities. Ongoing transactions with customers will throw light on the average value, frequency, nature, location, payment methods, and delivery channels associated with the business activities of the customer. Any business transaction that deviates from the risk rating of the customer requires a fresh risk assessment, suspicious activity report (SAR), or Suspicious Transactions Report (STR) filing with the UAE goAML portal.
No. Customer Due Diligence (CDD) requirements under the UAE AML laws apply only to Financial Institutions (FIs), Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs), and Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs).
Yes. As per the UAE AML laws, the Customer Due Diligence (CDD) procedures must be part of the AML Policy Manual of the company.
Reporting entities in UAE must consider the following risk factors while performing the risk assessment of customers:
- Type of business
- Source of Funds
- Source of Wealth
- The expected volume of cash transactions
- Nationality of customer
- Place of business of customer
- Place of residence of the customer
- Other criteria depending on the nature and size of business
The reporting entity should request an additional identification document in the following circumstances:
- When the identification document or photo is illegible or unclear
- When there is a signature difference between the KYC form and the documentary evidence submitted
- When the identification document is no longer valid due to its expiry
- For any other reason that the AML compliance officer deems fit to ask for the additional ID document.
Standard Due Diligence entails identifying the customer and verifying their identity. Reporting entities perform background checks on the customer and screen them against the sanctions list. They also perform adverse media searches and risk assessment for the customer. In the majority of the cases, reporting entities end up performing Standard Due Diligence as a part of their CDD program.
Enhanced Due Diligence entails additional verification for customers classified as high-risk customers or Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs). Such high-risk customers are more likely to get involved in money laundering or terrorist financing. Reporting entities in UAE adopt a risk-based approach while carrying out the due diligence of their customers. This approach requires additional control measures to be applied on a case-by-case basis.
In addition to standard due diligence requirements, reporting entities also obtain the following information while performing EDD:
- Source of Funds and or Source of Wealth
- Independent review of customer’s website and adverse media search
- Independent third-party confirmations if sufficient information is not available
- Reporting entities should also ascertain the legitimacy and credibility of the documents provided by the customer
- Lastly, senior management’s approval is obtained before entering into a transaction with a high-risk customer
The ongoing due diligence/transaction monitoring entails monitoring of business activities of the customers on a regular basis. Ongoing Due Diligence ensures that the transactions made by the customers are in sync with their risk profile. Ongoing transaction monitoring is an integral part of effective KYC Due Diligence.
In case of individual customers, the following information is obtained:
- Complete Name
- Address of the customer
- Contact numbers
- Additional/ alternative contact numbers
- Legit, accessible, and working email address
- Place of birth
- Date of birth
- Nationality
- Gender
- Government-issued identification number
- Occupation
- Signature
In case of legal entities, the following information is obtained as a part of the KYC and CDD process:
- Name of the entity
- Type of the entity
- Nature of business
- Date and place of establishment
- Information related to the board of directors
- Certificate of establishment/incorporation
- Information related to shareholders and ultimate beneficial owners
- Annual report for the previous year
- Information pertaining to senior management
Due to changes in circumstances, if a customer subsequently becomes a PEP or high-risk customer, then the AML compliance officer should carry out Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) and obtain senior management’s approval before entering into a transaction with such a customer.
As long as the requirements of the customer acceptance policy are met, a customer can be onboarded. If for some reason, the risks associated with a customer are beyond the risk appetite of the reporting entity, the AML compliance officer/MLRO should record his reasons in writing and reject the customer and also check if a suspicious transactions report or suspicious activities report needs to be submitted with the FIU UAE.
No. If the AML Compliance Officer is of the view that performing the KYC and CDD process would tip off a suspicious person then he may instead submit the Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) with the FIU UAE stating reasons why customer due diligence was not performed.
Screening customers on a daily basis helps identify instances like customers becoming sanctioned, PEPs, or high-risk and apply suitable control measures to remain compliant with the requirements of the AML/CFT Laws in UAE.
Customer name screening is one of the essential aspects of Customer Due Diligence (CDD) under the anti-money Laundering regulations of UAE. Accordingly, reporting entities in UAE must screen their customers, suppliers, and third parties regularly and perform name screening before entering into a new transaction. At a minimum, they have to perform sanction screening against the following lists:
- UNSC Sanctions List
- UAE Local Terrorist List
Reporting entities have to carry out due diligence on the outsourcing partner and ascertain their fitness for the purpose. Further, the third party must adhere to UAE AML/CFT laws. Reporting entity has to ensure that the third party is regulated and supervised, and adheres to the CDD measures towards Customers and record-keeping provisions. The reporting entity has to keep in mind that although the CDD function is outsourced, the primary responsibility to adhere to the AML/CFT laws in UAE remains with it, and it has to take reasonable measures to ensure data security and storage.
FIs, DNFBPs, and VASPs collect customer information, identify the customer and verify the documents collected. They also perform screening. The extent and detail of customer due diligence depend on the risks associated with the customer. Higher the risk, the higher the control.
Hence, based on customer profile, geography, nature of business, transactions, products, and services, a risk rating is assigned to the customer. If the customer happens to be a low-risk customer, simplified due diligence is performed. If the customer happens to be a low-medium risk customer, then standard due diligence is performed, and enhanced due diligence is performed for high-risk customers. The adoption of a risk-based approach in CDD helps reporting entities in channelizing their efforts in minimizing the risks. The risk-based approach helps ensure that the controls are in sync with the level of risk.
Reporting entities in UAE obtaining customer information, including their name, address, ID, date of incorporation, and information about partners/directors/shareholders, is an example of entities performing customer due diligence as per the requirements of AML/CFT laws.
The main difference between CDD and EDD lies in the extent of detailed verification performed by a reporting entity while carrying out customer due diligence. EDD entails a stricter customer verification process as compared to CDD, and it includes verification of source of funds and or source of wealth. Further, all high-risk customers and PEPs undergo an Enhanced Due Diligence Process where senior management’s approval is obtained before entering into a transaction with them.
The Customer Due Diligence information is used for:
- Identifying and verifying the customer and their transactions
- Identifying Beneficial Ownership
- Identifying the control structure of the company
- Monitoring transactions
- Assisting law enforcement by providing information pertaining to customers, activities, and transactions
Add a comment
About the Author
Pathik Shah
FCA, CAMS, CISA, CS, DISA (ICAI), FAFP (ICAI)
Pathik is a Chartered Accountant with more than 25 years of experience in compliance management, Anti-Money Laundering, tax consultancy, risk management, accounting, system audits, IT consultancy, and digital marketing.
He has extensive knowledge of local and international Anti-Money Laundering rules and regulations. He helps companies with end-to-end AML compliance services, from understanding the AML business-specific risk to implementing the robust AML Compliance framework.






