What is AML KYC compliance?
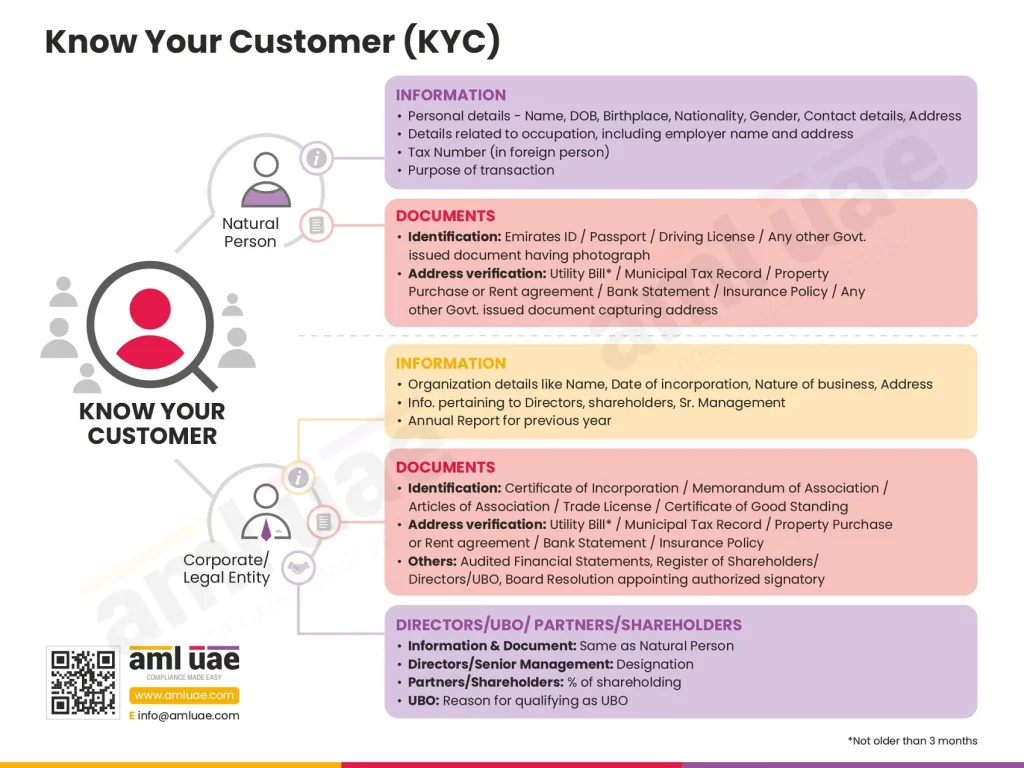
KYC is an abbreviated version of Know Your Customer. It is basically an important function that helps assess the risk-bearing power of your customers and legal abiding to comply with the laws of Anti-Money Laundering. Best practices for KYC Compliance majorly revolve around knowing the identity of your customers, the risk they possess, and their overall financial activities.
AML Best practices for KYC Compliance
Being a business owner, it is essential for you to know your customer well. If you are a financial institution or designated non-financial business or profession (DNFBP), you might face possible sanctions, reputational damage, and fines upon professionally collaborating with terrorists or money launderers.
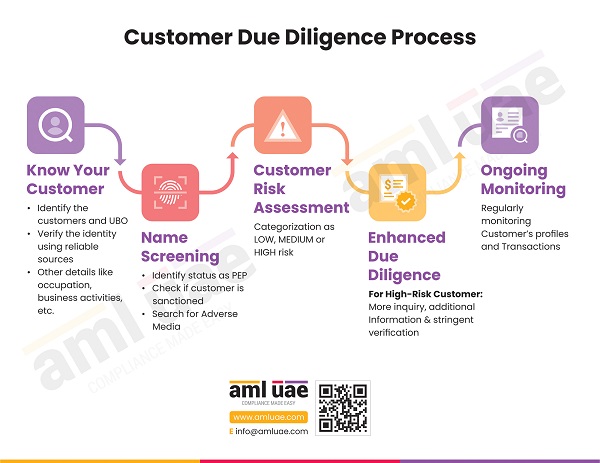
A KYC is basically a systematic process that any financial institution or business enterprise undertakes. This systematic process includes the following steps.
- Establishing the identity of the customer.
- Understanding the actual goal behind customer's activities. The ultimate motive behind this is to identify that the source of the customer's funds is both legally appropriate and legitimate.
- Effectively assess the risks associated with a particular or all the customers with the sole purpose of monitoring their activities.
- Dealers in precious metals and stones;Real estate agents and brokers;
Characteristics of an effective and best practice for KYC Compliance
To build and run an effective AML KYC strategy, you require the following elements.
1. Customer Identification Program or CIP
The only reason why the KYC process is conducted is to identify the legitimacy and authenticity of your customers. One of the most essential elements for successful and Best practices for KYC Compliance is to assess the risk of your customers. This risk assessment should be carried out at an individual level as well as on an institutional level. The Best practices for KYC Compliance provide qualitative guidance to determine the accurate risk level and the policies to mitigate those levels of risks.
- Name
- Address
- Contact number
- Nationality
- Date of birth
- Place of birth
- Occupation
- Employer name
- Purpose of transaction
- Beneficial owner
- Identification number
The procedures mentioned above are considered the core of the Best practices for KYC Compliance because, unlike other Anti-money Laundering compliance methods, this stands solid and reliable. The procedures need to be codified and clarified in order to provide guidance to executives, staff, and many other benefits to the regulators.
- The enterprise risk related to the risk exposure of the business itself
- Geographic risk related to the kind of countries a business deal with
- Product, service, or transaction-related risk
- Customer/business relationship-specific risk
- Channel related risk and
- Other risks
2. Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
For every financial institution, the only thing that matters is to identify whether you can trust the potential client or not. Customer Due Diligence is basically a critical element that effectively manages your risks and protects your company against terrorists, politically exposed parties (PEPs), and criminals who might involve a heavy risk quotient with them.
- Simplified Due Diligence (SDD) is basically the situation where the overall risk of terrorist financing or money laundering is relatively low, and customer due diligence is not required. Low-value accounts make the best example of SDD.
- Basic Customer Due Diligence is practically the information obtained for all the respective potential customers to verify their identity and assess the overall risk associated with that particular customer.
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is associated with potential high-risk customers. It is all about gathering additional information about your customers who carry a high-risk profile, verifying and evaluating the information to mitigate the associated risks.

- Ascertain the location and the identity of the potential customers and invest time to understand their basic business activities in-depth. It can be as easy as finding a legal document that verifies your potential customer's name and address.
- When authenticating a potential customer, identify their risk category and define what type of customer they are, and then store their information digitally
- Beyond basic customer due diligence, it is vital that you carry out various processes to ascertain whether there is room for enhanced due diligence. This could be an ongoing process because the existing customer might convert into high-risk profile customers over time. To avoid the cumbersome situations that may arise, it is better to conduct periodic due diligence assessments on all the existing customers. Following is the list of factors that you must keep in mind to identify the need for enhanced due diligence (EDD).
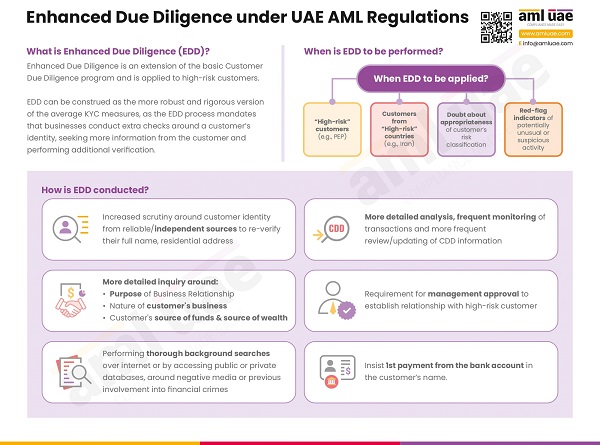
- Occupation of the customer
- Location of the customer
- Types of transactions
- Expected mode of payments
- Expected patterns in terms of the kinds of transactions, frequency of commerce, and the value of transactions
- Maintaining a record of all EDD and CDD performed on each customer is essential for regulatory audits
AML UAE will help you out in knowing your customers, both individuals or corporate houses, in terms of their risk profiles, nature of business, management, and ownership stakes so that you can remain compliant with UAE AML laws.
3. Ongoing monitoring
Monitoring your customers or potential customers once is not enough. You must develop an ongoing monitoring plan. The continuous monitoring function incorporates oversight of financial transactions and the thresholds developed to map the customer's risk profile.
Depending upon the risk profile of your customer, along with the risk mitigation strategies, you have to monitor a few additional factors.

- Spikes or surprisingly enhanced activities
- Unusual cross-border activities or trading with the black-listed geographies
- Inclusion of people on the sanctioned lists
- Adverse or negative media mentions
A business might be required to file a suspicious transaction report (STR) if the account's activities appear unusual.
The level of transaction monitoring depends on the risk-based assessment.
Corporate KYC for AML
Similar to individual accounts, corporate accounts also require KYC, identification, monitoring, and due diligence. The process of corporate account KYC is almost the same as of the individual KYC. However, the demands are different.
For corporate accounts, the volume of transactions increases along with the amounts per transaction, and several other risk factors are usually elevated, and hence more procedures are involved. These procedures are therefore known as Know Your Business (KYB).
Every jurisdiction has its own defined type of KYB requirements. However, there are four common steps that you can implement.

Retrieve the vitals of your company
Identify and verify the basic company information like registered number, address, name of the company, status, and the key management employees. On the other hand, it depends on your fraud prevention standards and jurisdiction when it comes to gathering specific information. You have to systematically collect all this information and cautiously feed it into your workflows.
Analyze the ownership structure
Identify the people who have ownership rights of the company through direct or indirect means. These can be individuals or a team of individuals.
Carry out AML/KYC checks
All the individuals you have identified as Ultimate Benefits Owners should undergo an AML or a KYC check.
Final words : AML KYC Best Practices
Knowing your customer is an integral part of your business. For businesses like auditors and accountants, lawyers, notaries, and other legal professionals, company and trust service providers, dealers in precious metals and stones (DPMS), real estate agents and brokers, the importance of AML KYC increases exponentially and should be performed thoroughly without a single casualty. Any error in the process can cause you qualitative as well as quantitative losses.
Our recent blogs
side bar form
Share via :
Add a comment
FAQs About AML KYC Compliance
About the Author
Pathik Shah
FCA, CAMS, CISA, CS, DISA (ICAI), FAFP (ICAI)
Pathik is a Chartered Accountant with more than 25 years of experience in compliance management, Anti-Money Laundering, tax consultancy, risk management, accounting, system audits, IT consultancy, and digital marketing.
He has extensive knowledge of local and international Anti-Money Laundering rules and regulations. He helps companies with end-to-end AML compliance services, from understanding the AML business-specific risk to implementing the robust AML Compliance framework.